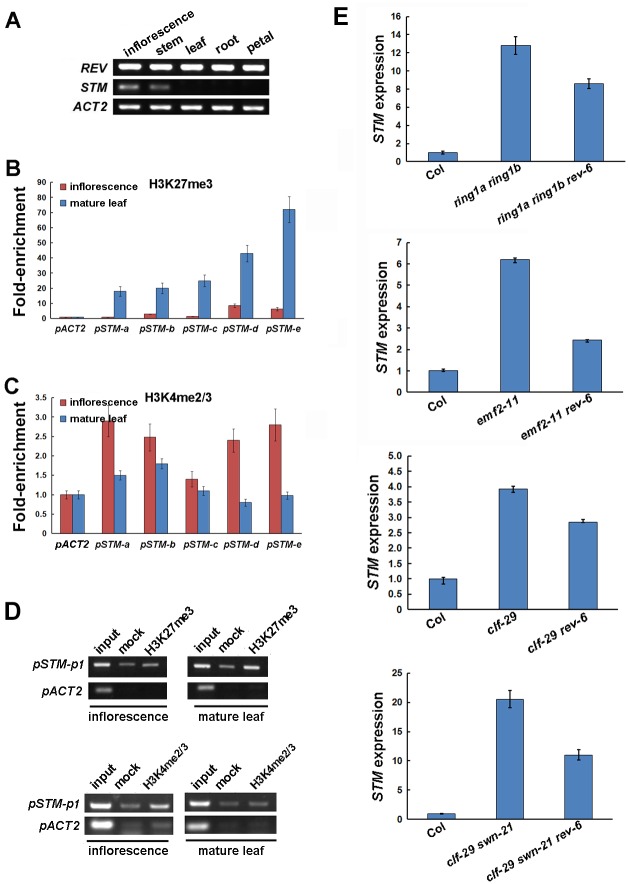
Fig 6. Epigenetic modification of the STM locus.
(A) RT-PCR with primers amplifying the REV, STM, or ACT2 coding regions on cDNAs generated from mRNA isolated from Col-0 wild-type inflorescence, stem, mature leaf (without the leaf axil region), root, and petal, respectively. ACT2 was used as a loading control. (B and C) Results of ChIP-qPCR performed on IP with antibodies against H3K27me3 (B) and H3K4me2/3 (C) on chromatin samples extracted from Col-0 wild-type inflorescences and mature leaves. The a-e regions (indicated as in Fig 5B) were assayed. Error bars indicate SD. More controls are shown in (D). (D) ChIP enrichment test by PCR with an anti-H3K27me3 antibody and an anti-H3K4me2/3 antibody using Col-0 wild-type inflorescences and mature leaves, together with total DNA input (input) and no-antibody (mock) controls. An ACT2 promoter region was used as a negative control. (E) Up-regulation of STM expression in mutants affecting PRC1 and PRC2 requires REV. RT-qPCR analysis of STM in whole seedlings of Col-0 wild type and mutants affecting PRC1 and PRC2 w/ or w/o rev-6. The vertical axis indicates relative mRNA amount compared with the amount in wild-type plants. Error bars indicate SD.