Fig. 7. Effect of expression of RbAp48-DN in the forebrain on CBP HAT activity.
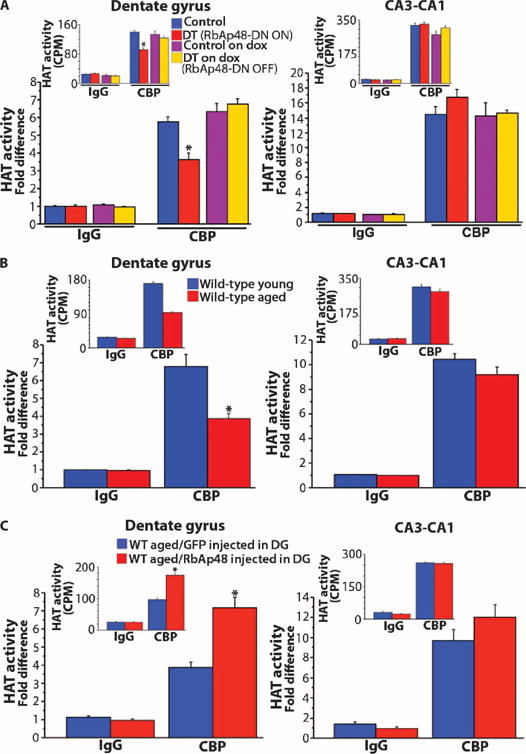
Averaged HAT activity (±SEM) of CBP immunoprecipitated from DG and CA3-CA1 lysates expressed as fold difference from IgG control immunoprecipitations. (Insets) Raw data acquired from HAT assays [3H counts per minute (CPM)]. (A) Assays in DT mice (3.5 months) and control littermates kept off doxycycline or doxycycline in adulthood. DT, DT off dox; Control, control off dox. n = 9 measurements per genotype per treatment (three measurements per immunoprecipitation per mouse; three mice per genotype per treatment). Significantly reduced CBP HAT activity in the DG of DT compared to all other groups (P < 0.0005, ANOVA). (B) Young (3.5 months) and aged (15 months) WT mice. n = 12 measurements per age (three measurements per immunoprecipitation per mouse; four mice per age). Significantly reduced CBP HAT activity in the DG of aged mice (P = 0.0006, ANOVA). (C) WT aged mice (15 months) virally expressing in DG RbAp48-HA (RbAp48 up-regulation in DG) or GFP (control). n = 9 measurements per virus (three measurements per immunoprecipitation per mouse; three mice per virus). CBP HAT activity was significantly increased in the DG of RbAp48-HA mice compared to GFP controls (P = 0.0001, ANOVA). *P < 0.0006. For detailed analysis, see table S3.
