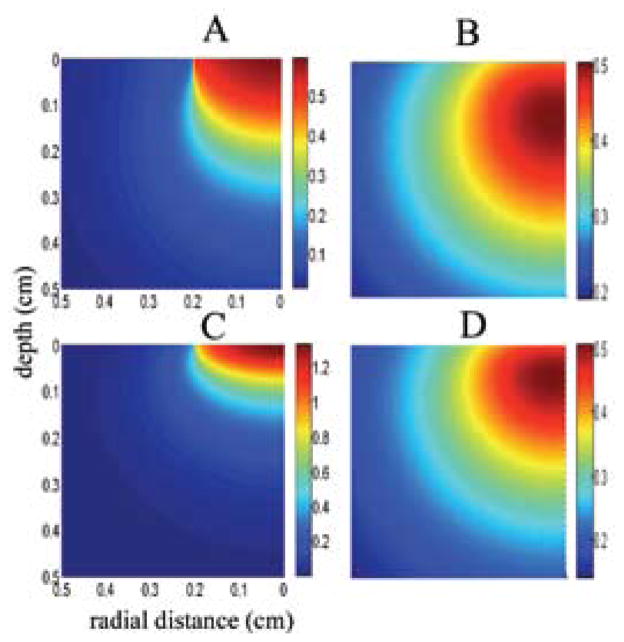
FIGURE 3.
Simulated NIR photon density (W/cm3) inside the human gray (A) and white (B) matters due to a 0.2 cm radius NIR beam and the resulting temperature elevations in the tissue (C for gray and D for white). The NIR light beam is aimed from the top to the center of the cylindrical volume with a radius of 0.5 cm. Because of cylindrical symmetry, plots are made only for one half of the vertical cross sectional area. Note that maximum temperature is observed not at the surface but at 1.2 mm and 0.7 mm below the surface, respectively. Absorption and scattering coefficients for human gray and white matters were adopted from Refs. 85 and 86 and thermal conductivity of gray (0.57) and white (0.5 Wm−1ºC−1) matters from Ref. 87.