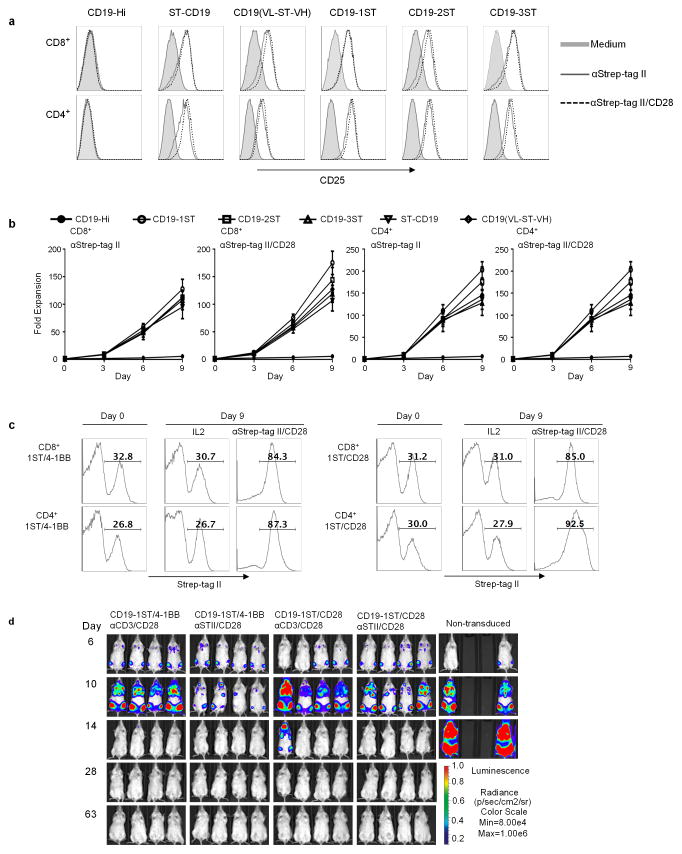
Figure 2. Activation, proliferation and function of Strep-tag CAR-T cells after stimulation with anti-Strep tag II mAb.
(a) CD4+ and CD8+ T cells expressing each of the CD19 CARs were sorted for EGFRt expression and stimulated with anti-Strep-tag II or anti-Strep-tag II/CD28 mAb–coated microbeads. After 48 h of stimulation, expression of the CD25 activation marker was determined by flow cytometry. Unstimulated cells (medium) were used as controls.
(b) Growth curves of Strep-tag CAR-T cells. FACS sorted EGFRt+ CD19 CAR-T cells (CD8+ and CD4+) were cultured with anti-Strep-tag II or anti-Strep-tag II/CD28 mAb coated microbeads in CTL media containing IL-2 (30–50 U/ml) and IL-15 (2 ng/ml) for 9 days. Aliquots of T cells were removed from the cultures for counting on days 3, 6, and 9 and the fold-increase in cell number determined. The data show the mean fold expansion obtained in three experiments with T cells from different donors.
(c) Stimulation of Strep-tag CAR-T cells with anti-Strep-tag II/CD28 beads induces selective outgrowth of transduced cells. CD8+ and CD4+ T cells were transduced with CD19 1ST/4-1BBζ and 1ST/CD28ζ CARs and 10 days later stimulated with anti-Strep-tag II/CD28 microbeads plus IL-2 or cultured with IL-2 alone for 9 additional days. The percentage of Strep-tag II positive cells at day 0 (before stimulation) and day 9 (after stimulation) were measured by flow cytometry. The results are representative of three experiments.
(d) Anti-tumor activity of CD19 1ST/4-1BBζ or 1ST/CD28ζ CAR-T cells in Raji-ffluc-bearing NSG mice. 2.5×106 CD19 CAR-T cells expanded with anti-CD3/CD28 beads or with anti-Strep-tag II/CD28 microbeads, and control non-transduced T cells were formulated in a CD8:CD4 ratio of 1:1 and infused into cohorts of NSG mice 7 days after inoculation with 0.5×x106 Raji/ffluc tumor cells. Tumor progression and distribution were evaluated by serial bioluminescence imaging.