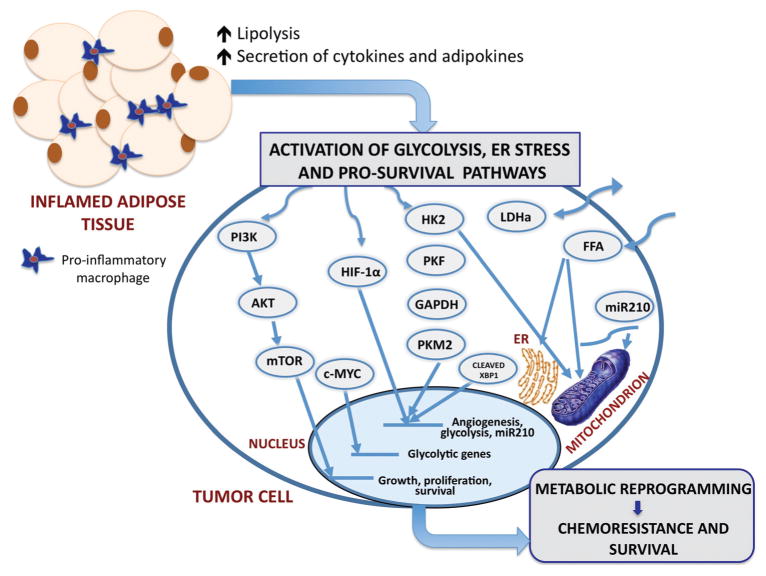
Figure 1.
The proposed schematic of possible mechanisms of metabolic regulation of tumor cells by dysfunctional adipocytes in obesity The major consequence of obesity is adipose tissue inflammation and associated increases in circulating levels of lipolysis-generated lipids and pro-inflammatory cytokines and adipokines. Through paracrine, autocrine, and endocrine effects, adipocyte-derived factors activate metabolic pathways in tumor cells and facilitating growth and survival. Pathways of interest include the following: phosphoinositol 3-kinase (PI3-K) signaling cascade, hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF-1α), increased glucose uptake and enhanced glycolysis, and the potentially oncogenic endoplasmic reticulum (ER stress) pathway. The stimulation of PI3-K pathway leads to downstream activation of Akt and mTOR, enhancing the transcription of genes involved in growth, proliferation and survival. PI3-K signaling can also activate c-MYC and lead to the induction of glycolytic genes. A potential crosstalk between the glycolysis pathway and the HIF-1α signaling axis potentiates HIF activity, and exacerbates the glycolytic and hypoxic phenotypes. HIF-1α signaling leads to the expression of miRNA-210, which disrupts mitochondrial integrity, affecting cellular metabolism. Additionally, FFA have the ability to disrupt mitochondrial and ER membrane integrity and cause mitochondrial dysfunction and ER stress. The interactions of the ER stress response protein, XBP-1, with HIF-1α drive the expression of HIF- and glycolysis-targeted genes. This adipocyte-driven dynamic network of events results in metabolic adaptation of tumor cells, implicating adiposity in tumor aggressiveness and chemoresistance to therapy. PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase; AKT, protein kinase b; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; c-MYC, myc proto-oncogene; HIF-1α, hypoxia-inducible factor 1; HK2, hexokinase 2; PKF, phosphofructokinase; GAPDH, glyceralaldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; PKM2, pyruvate kinase isoform; LDHα, lactate dehydrogenase; FFA, free fatty acids; miR-210, micro RNA 210.