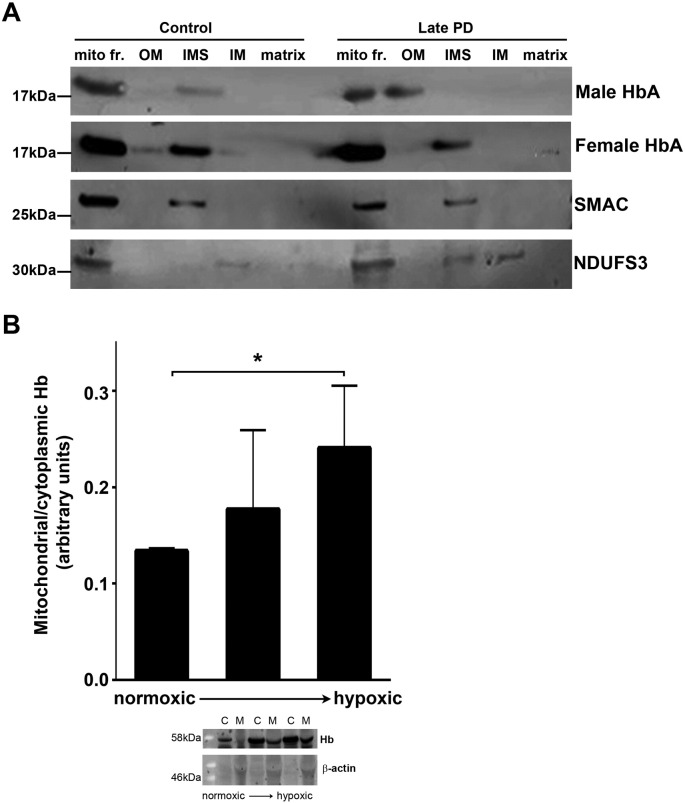
Fig. 1.
A. Mitochondrial HbA migrates from the intermembrane space to the outer membrane in affected human male cerebellum. Mitochondrial samples were sub-fractioned to allow examination of HbA localisation within the organelle, a representative gel is shown for each gender and control (total n = 8). The male Parkinson's disease brain demonstrated a shift in HbA localisation from the intermembrane space to the outer membrane fraction. This was not seen in the control or female Parkinson's brain mitochondria. Levels of HbA in the IMS were quantified in control and PD samples for both male and female patients (n = 2 for each), using Image J. Please see Supplemental Fig. 7 for all gel images.
Levels of HbA in the IMS were significantly decreased in male PD compared with male control (p = 0.028 using unpaired two-tailed t-test). No significant change in female PD compared with female control (p $_amp_$gt; 0.05, unpaired two-tailed t-test).
Mito fr – mitochondrial fraction, OM – outer membrane, IMS – inter membrane space, IM – inner membrane, M - matrix.
B. Cycles of hypoxia result in increased hb in Drosophila mitochondrial fractions. Mitochondrial/cytoplasmic Hb levels determined using Western blotting, normalised to beta-actin. Hypoxia conditions: 2.5% O2 30 min 25 °C followed by normoxia 30 min 25 °C (middle bar) 2.5% O2 30 min 25 °C followed by normoxia 30 min 25 °C × 2 (right hand bar). 40–100 flies per condition. n = 3, * p $_amp_$lt; 0.05 (1 tailed t-test).