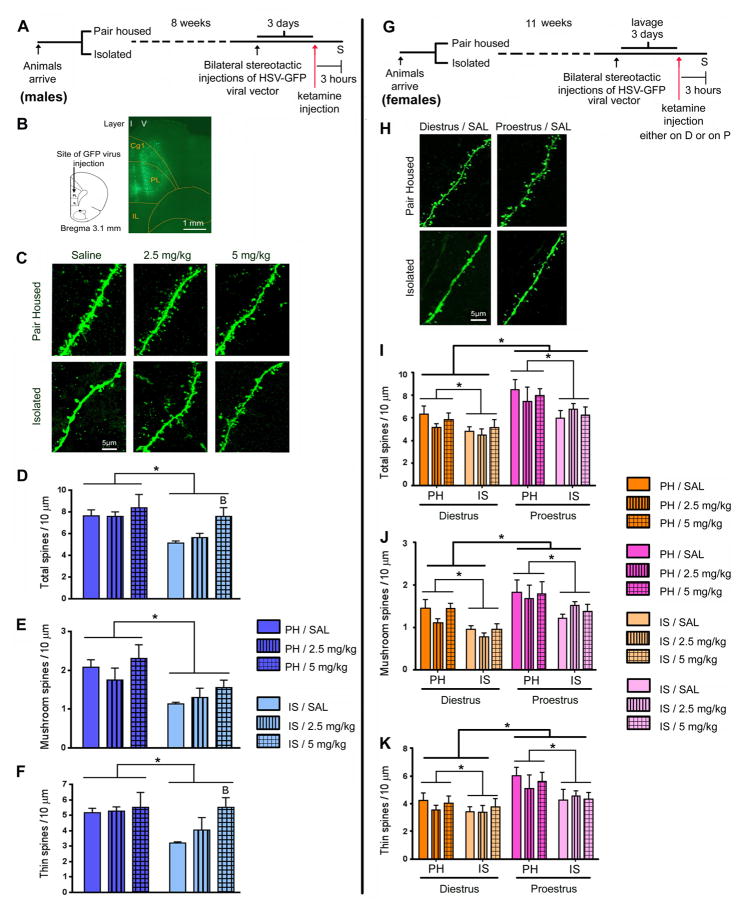
Figure 2.
Ketamine rescued IS evoked mPFC spine density deficits in males but not in female rats. (A) Schematic representation of the experimental design with male rats. Animals were grouped into PH and IS. After 8 weeks of stress, bilateral stereotactic injections of HSV-GFP were performed. After 3 days, when virus expression was at its maximum, animals were injected with ketamine. 3 hours after ketamine injection, animals were sacrificed (S). (B) Map of PL and IL regions in the mPFC of the rat, showing the site of injection of the HSV-GFP virus. GFP fluorescence was detected by immunostaining of sections. Shown is a low magnification (10x) fluorescence image of a GFP expressing mPFC section. Green fluorescence can be seen both in layer I (apical tuft) and in layer V (cell body) of the PL region of the mPFC. (C) Representative images are shown of high magnification Z-stack projections of proximal segments of the layer V pyramidal cell apical tuft dendrites of male rats (scale bar: 5 μm). (D) IS decreased spine density in the proximal segment of the apical tuft. This deficit was completely reversed by ketamine treatment (5 mg/kg) in male rats. Analysis of spine morphology revealed a decline in (E) mushroom and (F) thin spine density in IS animals. A single injection of ketamine (2.5 and 5 mg/kg) increased the density of (F) thin, but not (E) mushroom spines in the mPFC of male rats. (G) Schematic representation of the experimental design with female rats. Animals were grouped into PH and IS. Animals were lavaged for tracking of estrus cycle. After 11 weeks of grouping, bilateral stereotactic injections of HSV-GFP were performed. After 3 days, animals were injected with ketamine, either during diestrus (D) or proestrus (P). 3 hours after ketamine injection, animals were sacrificed (S). (H) Representative images are shown of high magnification Z-stack projections of apical tuft dendrites in female rats (scale bar: 5 μm). (I–K) IS evoked a significant decline in the density of spines of all sub categories in female rats irrespective of the cycle stage (effect of housing condition). (I) Total spine density, (J) mushroom as well as (K) thin spine densities were significantly lower in both PH and IS groups of female rats during diestrus than in proestrus (effect of cycle stage). However, in female rats, ketamine did not cause an increase in spine density in the mPFC. Density of spines was analyzed using Neurolucida Explorer (version 9; MBF Bioscience). Results are the mean ± SEM (~12 cells from four rats in each group; *p<0.05, Bp<0.05 compared to IS/SAL, two-way ANOVA, Fisher’s post-hoc test).