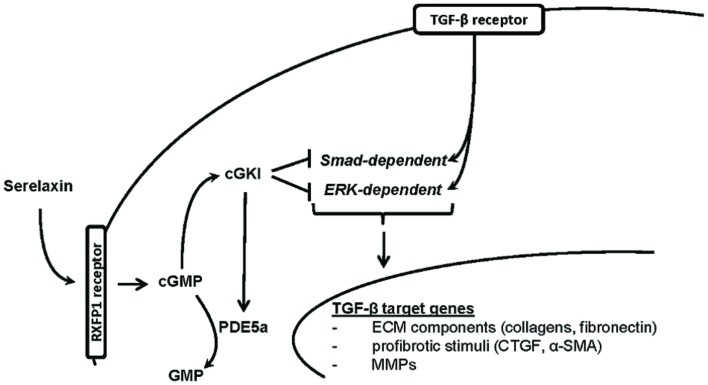
FIGURE 8.
Proposed hypothesis for in vivo antifibrotic signaling pathway of serelaxin in kidney. Serelaxin mediates its antifibrotic effect via RXFP1/cGMP/cGKI to inhibit TGF-β dependent Smad- and ERK-phosphorylation, which subsequently decreases ECM accumulation and suppresses profibrotic stimuli; α-SMA, α-smooth muscle actin; cGKI, cGMP-dependent protein kinase I; cGMP, cyclic guanosine monophosphate; CTGF, connective tissue growth factor; ECM, extracellular matrix; ERK, extracellular-signal regulated kinase; GMP, guanosine monophosphate; MMPs, matrix metalloproteinases; PDE5a, phosphodiesterase 5a; RXFP1, relaxin family peptide receptor 1; Smad, small mothers against decapentaplegic protein; TGF-β, transforming growth factor-β.