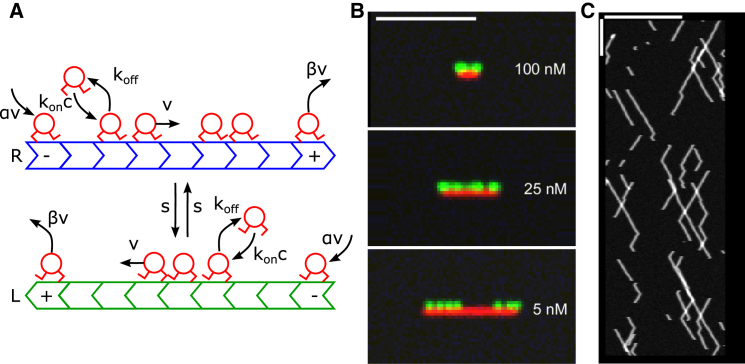
Figure 1.
Model and results overview. (A) Schematic of the model of motor motion on an antiparallel microtubule overlap. Two filaments (green and blue) are modeled as one-dimensional lattices with their plus-ends oppositely oriented. The filaments are labled R (L) if the plus end is pointing to the right (left). Motors (red) bind to empty lattice sites with rate and unbind with rate . Bound motors step toward the MT plus-end with rate v (if the adjacent site toward the MT plus-end is empty) or switch to the other MT with rate s (if the corresponding site on the adjacent MT is empty). At MT minus ends, motors are inserted at rate αv. At MT plus ends, motors are removed at rate βv. (B) Simulated experimental images made from our kMC model. (Green) Motor density. (Red) Overlap region. Scale bar, 5 μm. Simulations used to generate these images used the reference parameter set (Table 1) and the indicated bulk motor concentrations. (C) Simulated kymograph made from our kMC model with motor spatial position on the horizontal axis and time increasing downwards. Horizontal scale bar, 10 μm. Vertical scale bar, 5 s. The simulations used to generate the kymograph used the reference parameter set and 0.5 nM bulk motor concentration. To see this figure in color, go online.