Figure 6.
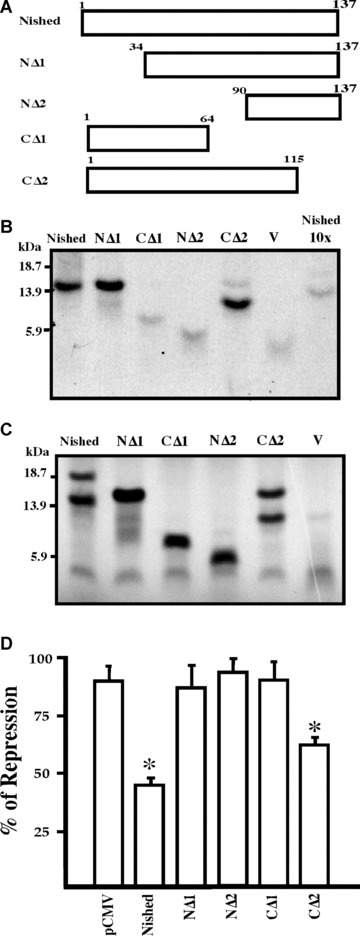
Schematic representation of Nished and its C‐and N‐terminal deletion mutants. (A) The deletions were made and cloned in the mammalian expression vector, pcDNA6V5/HisB, as described in ‘Material and Methods’. Numbers denote the amino acids in the constructs. (B) microaffinity isolation of S35 methionine labelled Nished and its N and C‐terminal deletion proteins generated by coupled transcription‐translation reaction with biotinylated CSS oligonucleotide as described in ‘Material and Methods’. (C) One tenth of reaction mixture volume of S35 methionine labelled Nished and its N‐and C‐terminal deletions proteins were electrophoresed on an 18% SDS gel. (D) Functional analysis of Nished deletion mutants. Primary skeletal muscle cells were co‐transfected with the IRE mutant (pMutIRELuc and Nished or the N and C terminal deletions mutants). The luciferase activity was normalized against the internal control, Renilla luciferase activity. (n= 7 in triplicate, □ one sample t‐test with Bonferroni correction, P < 0.05). Nished full length protein; NΔ1 (34–137 a.a); NΔ2 (90137 a.a.); CΔ1 (1–64 a.a); CΔ2 (1–115 a.a); V, Vector alone (negative control); Nished 10X, competition with lysate contouring vector alone.
