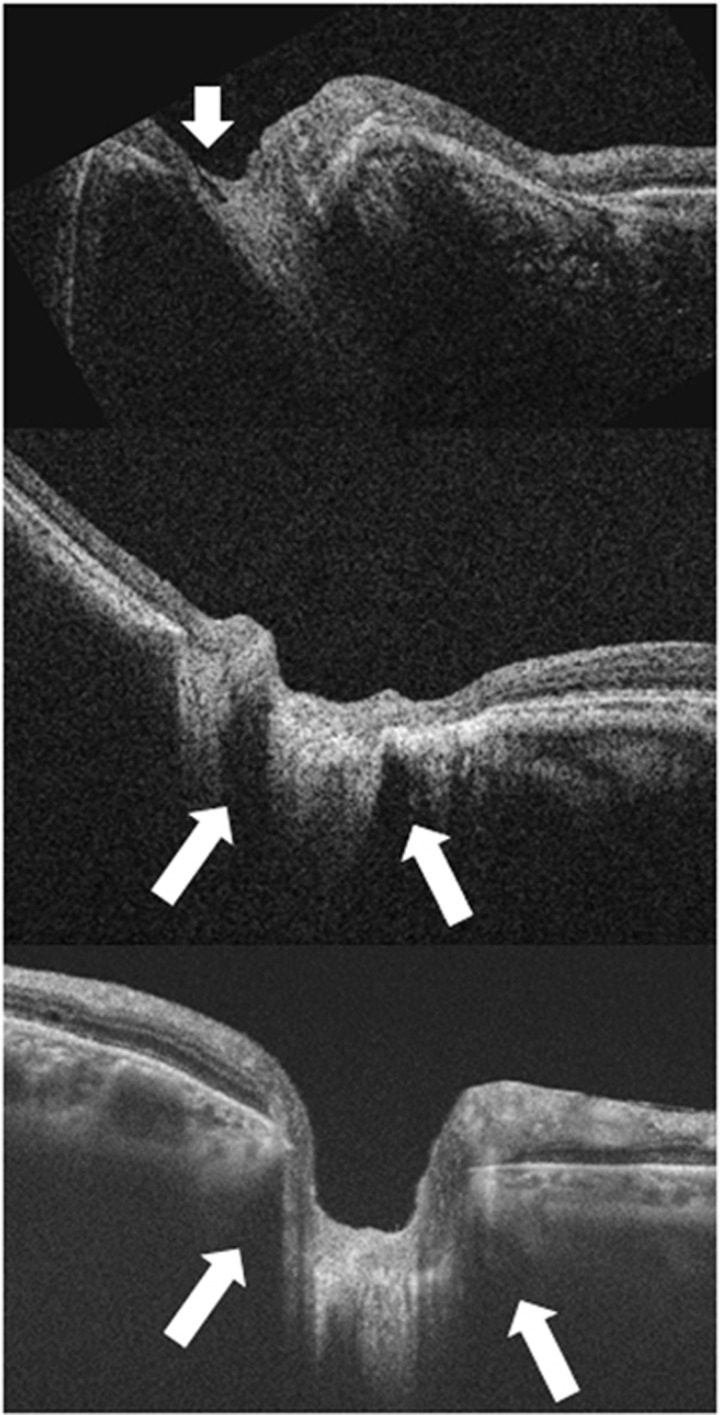
Figure 4.
Enlargement of the optic nerve head in highly myopic eyes occurs due to stretching of the scleral canal and lamina cribrosa. The lamina is torn from the peripapillary sclera and eventually the overylying nerve fiber is disrupted, and this stage is observed as optic disc pits, especially at the superior and inferior poles of the optic disc. Top: optical coherence tomography (OCT) shows a hyporeflective gap indicating the acquired pit of the optic nerve (white arrow). Middle: OCT shows the subarachnoid spaces as hyporeflective triangular spaces along both the upper and lower borders of the optic nerve (white arrows). The elongated dural attachment at posterior scleral canal in highly myopic eye leads to widening of retrobulbar subarachnoid spaces comparing with that observed in an ametropic eye (Bottom).