Figure 2.
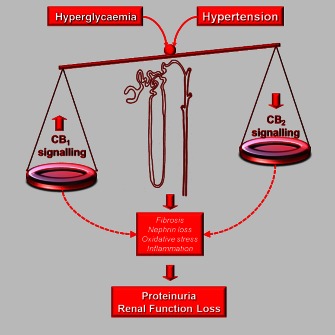
Opposing effects of CB1 receptor and CB2 receptor in DN. The CB1 receptor has deleterious pro‐oxidative and pro‐inflammatory effects, while opposing protective effects are induced by CB2 receptor activation. In diabetes, hyperglycaemia and hypertension alter the balance between CB1 receptor and CB2 receptor signalling as CB1 receptor expression is enhanced, while CB2 receptor is down‐regulated. This imbalance favours oxidative stress, inflammatory and profibrotic processes and contributes to the development of proteinuria by enhancing nephrin loss and of renal function loss by exacerbating fibrogenesis in both the mesangium and tubulointerstitium.
