Figure 5.
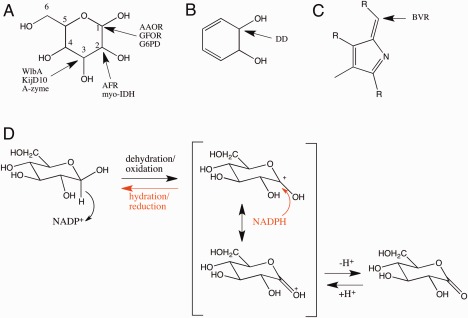
The positions of the substrate carbons in which a hydride is abstracted (oxidation) or added (reduction) in different type of enzymes. (A) pyranose ring, (B) trans‐dihydrodiol, (C) biliverdin. (D) The representative reaction mechanism for D‐glucose oxidation and D‐glucono‐1,5‐lactone reduction. NADP+ or NADPH is a key catalytic part of the enzyme. Depending on the enzyme amino acid residues may participate in the deprotonation/protonation step.
