Figure 6. Effects of WTD on the temperature of the articular surface and the blood flow volume in CIA rats.
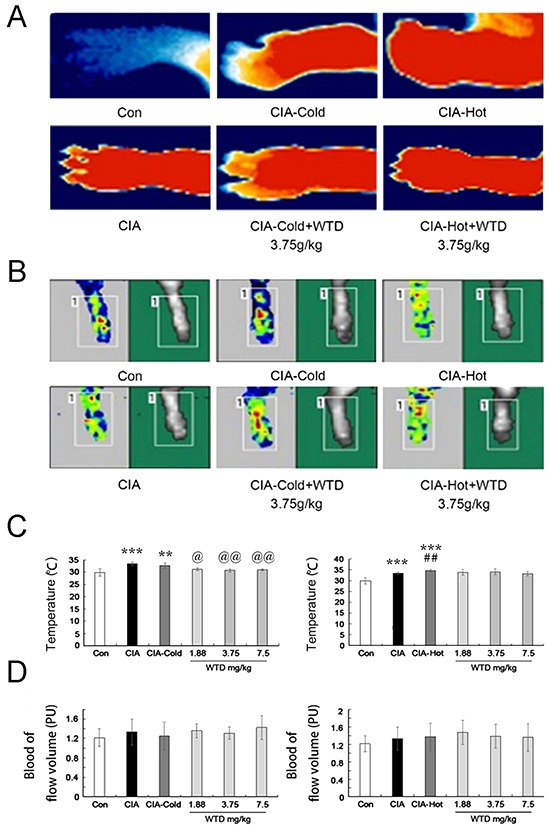
A. The temperature of the articular surface in CIA, CIA-cold/hot model groups were markedly increased compared with the control group, while doses of 3.75 g/(kg•day) WTD significantly decreased the temperature in both the CIA-cold /hot model groups; B. Blood flow volume in the joints tend to increase in the CIA, CIA-cold/hot model groups compared with the control groups, and doses of 3.75 g/(kg•day) WTD increased the blood flow volume in both the CIA-cold/hot model groups; C. The temperature of the articular surface were markedly up-regulated in the CIA, CIA-cold/hot model groups, which were markedly reversed by low-high doses of WTD in the CIA-cold groups. No statistical significance was observed in the CIA-hot model groups; D. WTD could increase the blood flow volume in the joints in both the CIA-cold/hot model groups without a significant difference. Data are represented as the mean±S.D (n=16). *, **, and ***, P<0.05, P<0.01, and P<0.001, comparison with the control group. #, ##, ###, P<0.05, P<0.01, and P<0.001, comparison with the CIA model group. @, @@, @@@, P<0.05, P<0.01, and P<0.001, comparison with the CIA-cold/hot model groups.
