Figure 1. B19 inhibits cells growth and induces accumulation of Intracellular ROS in human gastric cancer cells.
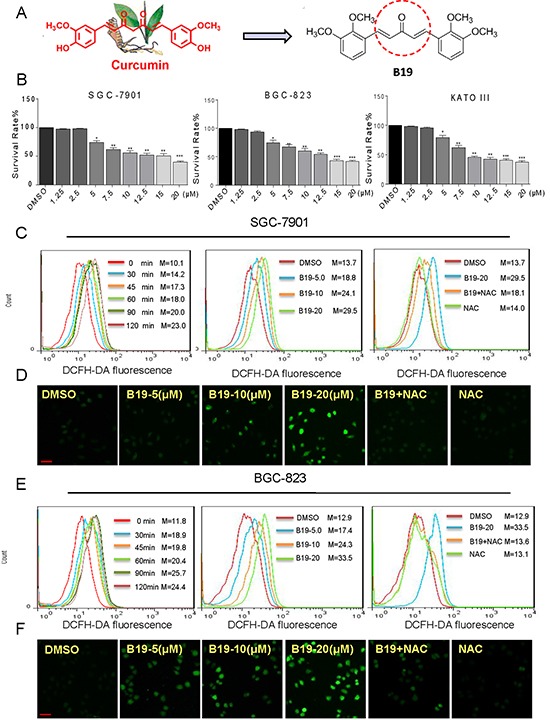
A. Chemical structure of curcumin and B19. B. Effects of B19 in human gastric cancer cell viability. Cells were treated with concentration gradient of B19 for 24h and processed for MTT assay. C, E. Intracellular ROS generation time- and dose-dependently induced by B19 was measured in SGC-7901 cells and BGC-823 cells by staining with DCFH-DA (10 μM) and flow cytometry analysis. SGC-7901 cells and BGC-823 cells were treated with B19 (20 μM) for the indicated times. SGC-7901 cells and BGC-823 cells were pre-incubated with or without 5 mM NAC for 2 h before exposure to B19 at the indicated concentrations for 30 min. Then, Intracellular ROS generation was measured by flow cytometry. D, F. Intracellular ROS generation induced by increasing doses of B19 for 30 min was measured in SGC-7901 cells and BGC-823 cells by fluorescence microscope. SGC-7901 cells and BGC-823 cells were pre-incubated with 5 mM NAC for 2 h before exposure to B19 (20 μM) for 30 min. Intracellular ROS generation was measured by fluorescence microscope. A scale bar, 20μm. All images shown here are representative of three independent experiments with similar results. Error bars represent S.E.M. of triplicates (*P< 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001).
