Figure 1. Chemical structures and general synthetic scheme used to obtain the EphA2 targeting agents conjugated with gemcitabine.
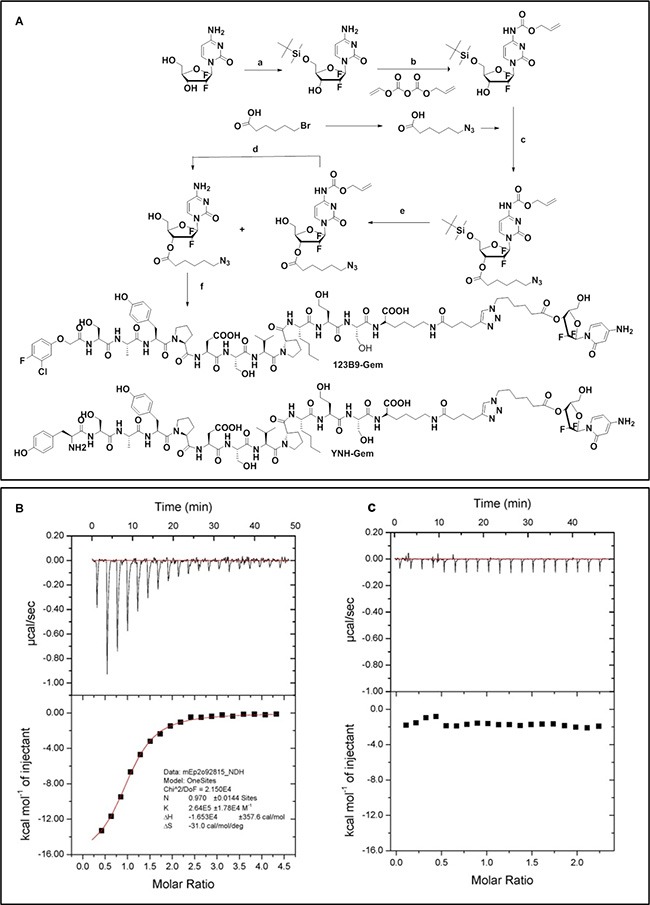
(A) Synthetic scheme. Regents and condition: a TBSCl, imidazole, rt, 12 h; b Diallyl pyrocarbonate, Et3N, THF, rt, 12 h; c 6-azido-hexanoic acid, EDCI, DMAP, DCM, rt, 6 h; d TBAF, THF, rt, 2 h; e (Ph3P)2PdCl2, Bu3SnH, HOAc, THF, 0°C, 2 h; f YNH motif or 123B9 motif (Supplementary Figure S1), CuSO4, sodium ascorbate, DMSO/water, rt, 48 hf) YNH motif or 123B9 motif, CuSO4, sodium ascorbate, DMSO/water, rt, 48 h. YDH-L2-Gem has the same composition as YNH-L2-Gem except that it contains a scrambled peptide of sequence YDPS(Hsr)A(Nle)YSPSVK and it was synthesized using the same general scheme. Analytical data relative to critical intermediates and final compounds are reported as Supplementary Figure S4. Isothermal titration calorimetry data for YNH-L2-GEM against (B) EphA2 and (C) EphA3 LBD ligand binding domains are reported. For the binding between EphA2 LBD and YNH-L2-GEM the data revealed a Kd = 3.8 μM, ΔH = −16 Kcal/mol, −TΔS = −9.1 Kcal/mol. No appreciable binding was detected between YNH-L2-GEM and the EphA3 LBD (∼50% sequence identity with the EphA2 LBD). Similar data were obtained with 123B9-L2-GEM (Supplementary Figure S1).
