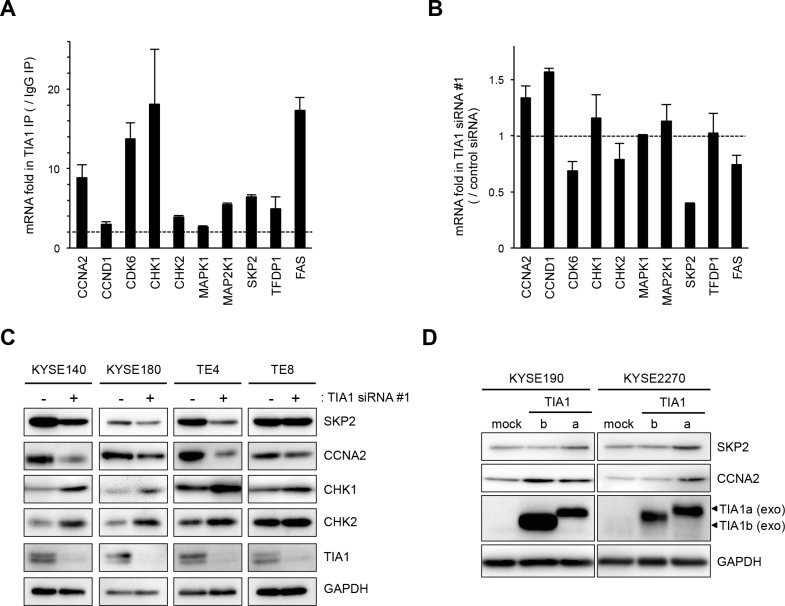
Figure 5. Binding of TIA1 with mRNAs of putative target mRNAs and its effect on protein levels in ESCC cells.
(A) Bindings between TIA1 and the nine putative target transcripts encoding cell cycle regulatory proteins identified through RIP-chip and RIP-seq (Supplementary Table S5) using anti-TIA1 antibody, as well as the known target, FAS mRNA, were validated by qPCR after RIP using KYSE180 cells. TIA1-mRNA bindings were measured by RIP followed by qPCR amplification and expressed as the enrichment of individual mRNAs in the TIA1 IP relative to an IgG IP. The data were normalized to the levels of GAPDH mRNA, an abundant mRNA that is not a target of TIA1 and that is present as a low-level co-precipitated contaminant in all IP samples. Representative results (mean ± SD, n = 3) of four independent experiments are shown. (B) Effects of TIA1 silencing on the expression of putative target mRNAs in ESCC cells. KYSE180 cells were transfected with 10 nM TIA1-specific or control siRNA for 48 h. The amounts of the 10 target mRNAs were measured by qPCR using GAPDH mRNA as an endogenous control. The values are expressed as fold changes (mean ± SD, n = 3) compared with the respective values in control siRNA-transfected cells. (C) Effects of TIA1 silencing on the expression of proteins encoded by the putative target genes in ESCC cells. KYSE140, KYSE180, TE4, or TE8 cells were transfected with 10 nM TIA1-specific or control (−) siRNA for 48 h. The levels of SKP2, CCNA2, CHK1, CHK2 and TIA1 proteins were measured by western blot analysis using GAPDH as a loading control. (D) Effects of exogenous overexpression of each TIA1 isoform on the expression of proteins encoded by putative target genes in ESCC cells. Lysates were prepared from KYSE190 or KYSE2270 cells overexpressing TIA1. The levels of SKP2, CCNA2 and exogenous TIA1 proteins were measured by western blot analysis using GAPDH as a loading control.