Figure 7. The rational for adding Anti PD-L1 monoclonal antibody to BRAFi treatment.
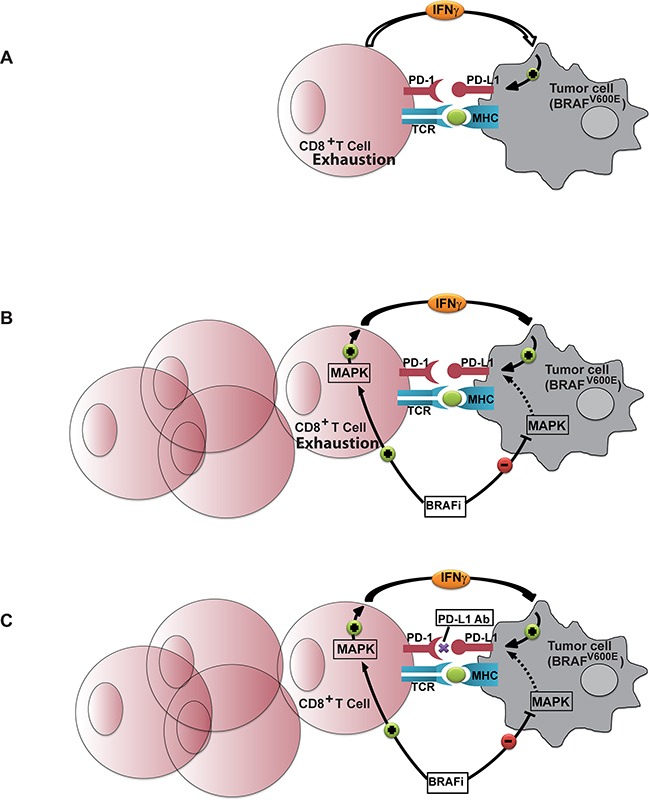
A. In the naïve environment the lack of migration of T-cells into the tumor site and the mild reactivity that drives T-cells to produce cytokine (among them IFNγ) has substantial impact on the expression of PD-L1 which tempers the already weak anti tumor reaction. B. BRAFi treatment results in increased T cell infiltration into the tumor microenvironment. Although BRAFi potentially down-regulates the expression of PD-L1 on BRAFV600E tumor cells by down regulating MAP kinase activity in these cells, it paradoxically up-regulates MAP kinase in the BRAFWT T-cells which results in IFNγ production and intensive up-regulation of PD-L1 on tumor cells. Immune response with BRAFi alone therefore does not come to its full potential. C. Adding anti PD-L1 antibody is an additional step necessary to allow the immune response facilitated by BRAFi to reach its full potential.
