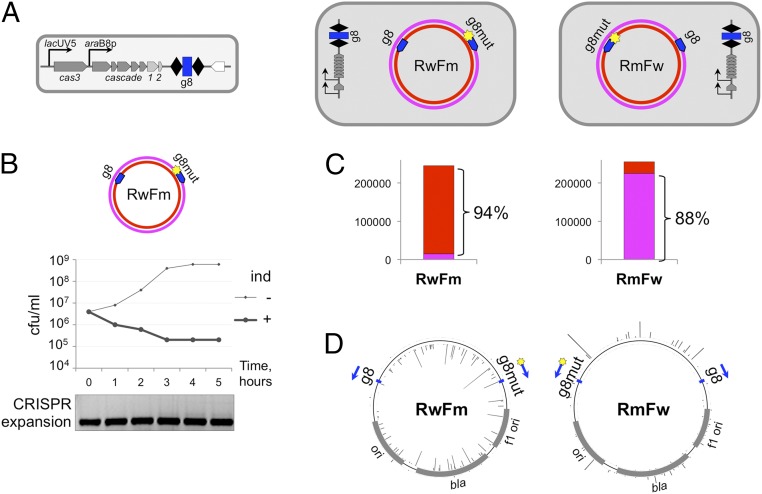
Fig. 4.
CRISPR adaptation from matching and partially matching protospacer targets located in an in cis configuration. (A) The E. coli KD263 cells transformed with pT7Blue-based RwFm or RmFw plasmids carrying a wild-type and a mutant, C1T, version of the g8 protospacer on different strands are schematically shown at the top. (B) A graph showing the number of CFUs on LB plates containing ampicillin in KD263 cultures transformed with one of the plasmids shown in A with or without induction of cas gene expression. Shown below are the results of agarose gel electrophoresis of PCR amplification products obtained from aliquots of induced culture with primers annealing at the g8 spacer and further upstream in the KD263 CRISPR array leader. (C) Bar graphs showing the overall statistics of acquired spacers in each cell culture shown in A with spacers mapped to either plasmid DNA strand shown in different colors (color coded as in plasmid schematics in A). (D) Mapping of spacers acquired by KD263 cells transformed with RwFm or RmFw. The positions of priming protospacers are shown by blue arrows.