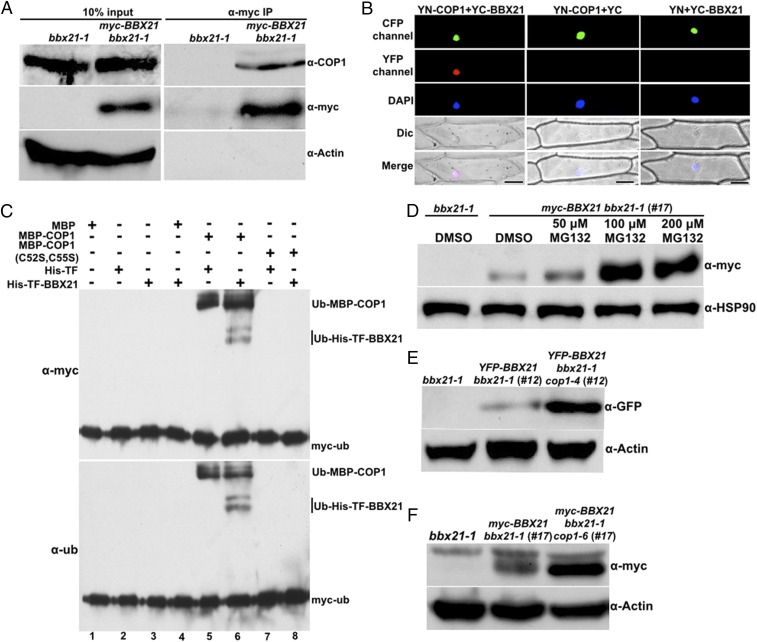
Fig. 1.
BBX21 is controlled by COP1 in dark-grown seedlings. (A) Co-IP analysis showing that BBX21 interacts with COP1 in vivo. Four-day-old white light-grown bbx21-1 and myc-BBX21 bbx21-1 (#17) seedlings were transferred to darkness for 16 h and then subjected to a co-IP assay using anti-myc antibodies, with the immunoprecipitates detected using anti-COP1 and anti-myc antibodies, respectively. Actin served as a negative control. (B) BiFC assay showing the interaction of BBX21 with COP1 in onion epidemal cells. Full-length COP1 and BBX21 were fused to the split N- or C-terminal fragments of YFP (YN-COP1 or YC-BBX21). Nuclear localized CFP-CSU1 served as a marker for successful transfection. Unfused YFP N-terminal (YN) or C-terminal (YC) fragments served as negative controls, as indicated. DAPI staining marked the positions of nuclei. Dic, differential interference contrast in light microscope mode; Merge, merged images of YFP channel, DAPI, and Dic. (Scale bar: 100 μm.) (C) COP1 ubiquitinates BBX21 in vitro. Ubiquitination assays were performed in a reaction mix containing UBE1 (E1), rice 6×His-Rad6 (E2), and myc-tagged ubiquitin (myc-Ub). Ubiquitinated MBP-COP1 and 6×His-TF-BBX21 were detected by anti-ubiquitin and anti-myc monoclonal antibodies, respectively. The “+” and “−” indicate presence and absence, respectively. (D) Immunoblot analysis of myc-BBX21 protein levels in dark-grown myc-BBX21 bbx21-1 (#17) transgenic seedlings treated with DMSO or various concentrations of MG132 (50, 100, or 200 μM) for 3 h. (E) Immunoblot analysis of YFP-BBX21 protein levels in YFP-BBX21 bbx21-1 (#12) and YFP-BBX21 bbx21-1 cop1-4 (#12) transgenic seedlings grown in the dark for 4 d. (F) Immunoblot analysis of myc-BBX21 protein levels in myc-BBX21 bbx21-1 (#17) and myc-BBX21 bbx21-1 cop1-6 (#17) transgenic seedlings grown in the dark for 4 d. In D–F, bbx21-1 served as a negative control, and anti-HSP90 or anti-actin served as a loading control.