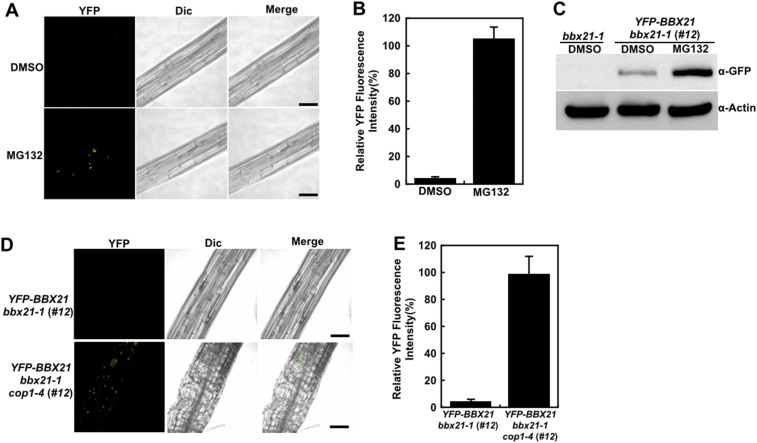
Fig. S3.
COP1 controls BBX21 abundance in dark-grown seedlings. (A) Hypocotyl cells of dark-grown YFP-BBX21 bbx21-1 (#12) seedlings treated with DMSO or 100 μM MG132 for 3 h analyzed by fluorescence microscopy. (B) Relative YFP fluorescence intensity in hypocotyls of YFP-BBX21 bbx21-1 (#12) transgenic seedlings treated with DMSO or 100 μM MG132 for 3 h. (C) Immunoblot analysis of YFP-BBX21 protein levels in dark-grown YFP-BBX21 bbx21-1 (#12) transgenic seedlings treated with DMSO or 100 μM MG132 for 3 h. bbx21-1 served as a negative control, and anti-actin served as a loading control. (D) Analysis of YFP-BBX21 in hypocotyl with fluorescence microscopy. YFP-BBX21 bbx21-1 (#12) and YFP-BBX21 bbx21 cop1-4 (#12) transgenic seedlings were grown in the dark for 4 d. (E) Relative YFP fluorescence intensity in hypocotyls of YFP-BBX21 bbx21-1 (#12) and YFP-BBX21 bbx21-1 cop1-4 (#12) transgenic seedlings grown in the dark for 4 d. In A and D, the pictures are representative images taken from the hypocotyls. YFP, YFP channel image; Dic, differential interference contrast in light microscope mode; Merge, merged images of YFP and Dic. (Scale bar: 50 μm.) In B and E, data were obtained from two independent experiments. At least 10 seedlings were measured each time. Fluorescence intensity was measured using Image J software.