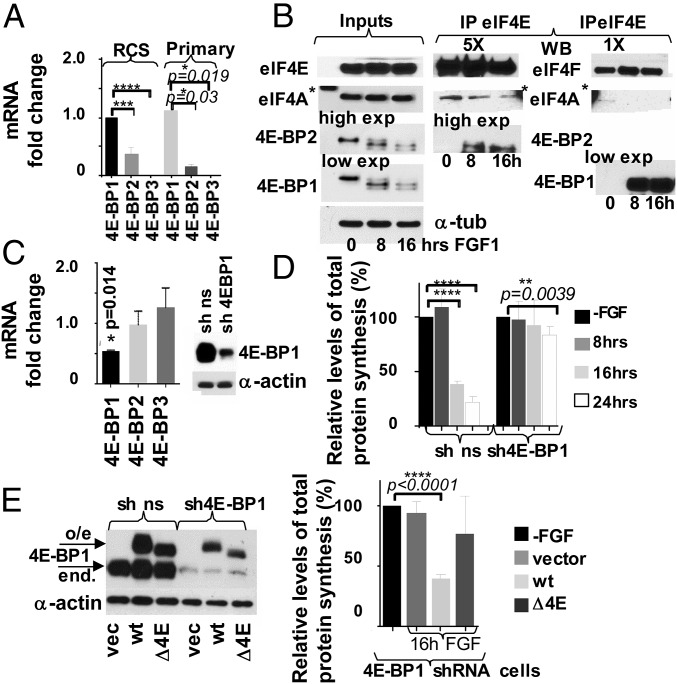
Fig. 5.
The 4E-BP1 activity is crucial for mediating growth arrest in chondrocytes. (A) Relative levels of 4E-BP1-3 mRNAs in chondrocytes were determined by qRT-PCR. The 18S was used as a normalization control. (B) FGF signaling stimulates 4E-BP1/eIF4E and 4E-BP2/eIF4E complex formation. RCS cells were treated with FGF1, and protein extracts were incubated with agarose-conjugated eIF4E antibody. Five times more (5X) of the IPs were loaded to visualize 4E-BP2 in eIF4E IPs compared with the 4E-BP1 detection. The asterisk denotes an unspecific band caused by a protein marker. 5X and 1X eIF4A and eIF4E are the same exposure. (C–E) RCS cells were infected with either 4E-BP1 or nonsilencing (ns) shRNAs. (C) Relative levels of 4E-BP1-3 mRNAs in sh4E-BP1 cells compared with the control cells. Five micrograms of total protein were analyzed by WB. (D) Protein synthesis was measured by S35-Met/Cys incorporation. The data are representative of three independent experiments, and error bars represent mean ± SD. (E) Overexpression of wt4E-BP1 but not a 4E-BP1 mutant deficient in eIF4E binding (ΔE4E-BP) restores FGF response in the cells with low levels of 4E-BP1 (4E-BP1 shRNA cells). Five micrograms of total protein were analyzed by WB to validate protein expression. Protein synthesis was measured by S35-Met/Cys incorporation. The data are representative of three independent experiments.