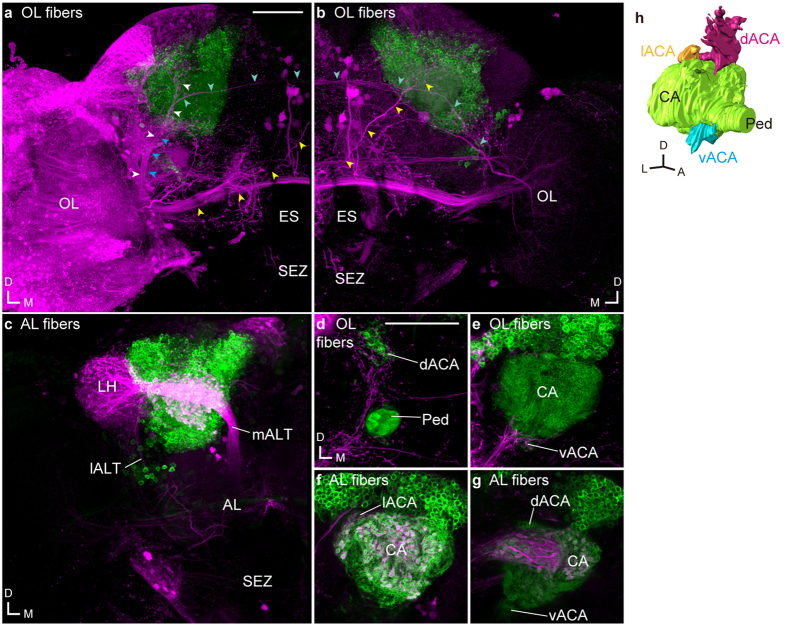
Figure 1. Sensory pathways visualized by dextran injection into the primary sensory center in Drosophila.
Dextran conjugated with tetramethylrhodamine and biotin (magenta) was injected into the optic lobe (OL, (a,b)) or antennal lobe (AL, (c)) in flies expressing GFP (green) in Kenyon cells with OK107-GAL4. White, blue, and yellow arrowheads indicate the OLCT1, OLCT2, and OLCT5, respectively. Some OLCT2 neurons also innervate the contralateral hemisphere (cyan arrowheads). (d–g) The accessory calyces innervated by the labeled cells from the OL (d,e) and AL (f,g). (h) The oblique view of the mushroom body calyx labeled with OK107-GAL4. Green, magenta, yellow, and cyan represent the main calyx and pedunculus, dorsal, lateral, and ventral accessory calyx, respectively. The position of the lateral ACA was determined with the anti-SYNAPSIN signals. Scale bars = 50 μm. A, anterior; AL, antennal lobe; CA, main calyx; D, dorsal; dACA, dorsal accessory calyx; ES, esophagus; L, lateral; lACA, lateral accessory calyx; lALT, lateral antennal lobe tract; LH, lateral horn; M, medial; mALT, medial antennal lobe tract; OL, optic lobe; Ped, pedunculus; SEZ, subesophageal zone; vACA, ventral accessory calyx.