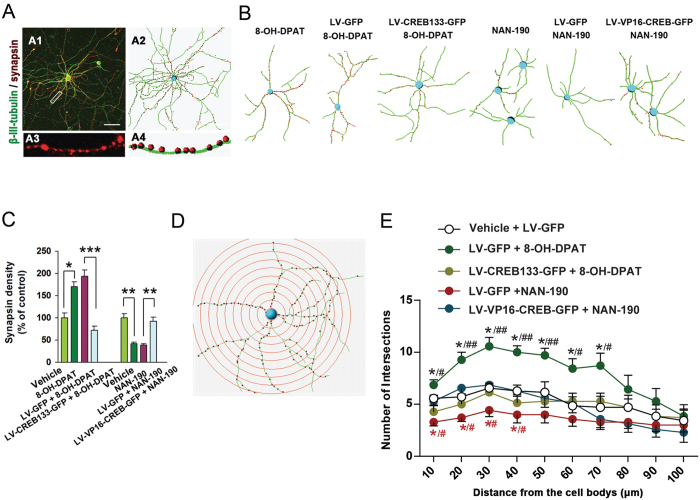
Figure 3. CREB activation is essential for the role of 5-HT1aR in modulating synapsin density and dendrite growth.
(A) Representative immunofluorescence of synapsin and β-III-tubulin (A1) from the cultured hippocampal neurons and simulated diagram view of processes (A2). A high magnified image (A3) and simulated diagram view (A4) from a selected area in A1. Scale bar = 50 μm. (B) Simulated diagram views of β-III-tubulin and synapsin immunofluorescence from the cultured hippocampal neurons exposed to different treatments. (C) Summarized assay of density of synapsin in (B). (n = 6). (D) A representative simulated diagram view of sholl analysis of dendritic complexity from the hippocampal neurons. (E) Sholl analysis of dendritic complexity of the cultured hippocampal neurons exposed to different treatments in (B). (n = 7). Means ± SEM. In C, *P < 0.05 **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001; in E, *(black)P < 0.05, LV-GFP + 8-OH-DPAT vs LV-GFP + vehicle; *(red)P < 0.05, LV-GFP + NAN-190 vs LV-GFP + vehicle; #(black)P < 0.05, ##(black)P < 0.01, LV-CREB133-GFP + 8-OH-DPAT vs LV-GFP + 8-OH-DPAT; #(red)P < 0.05, LV-VP16-CREB-GFP + NAN-190 vs LV-GFP + NAN-190.