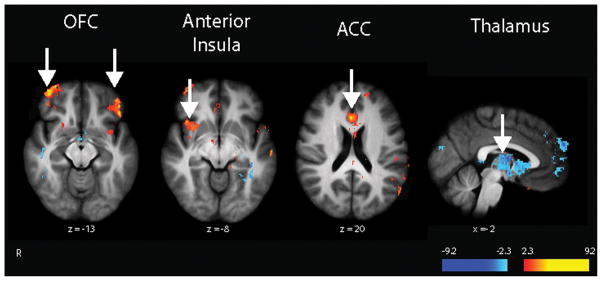
Figure 1.
Mindfulness meditation–based pain relief is associated with multiple brain mechanisms. Regression analyses corresponding to those in Zeidan et al.21 revealed that reductions in mindfulness meditation–induced pain intensity were associated with greater activation (depicted in red) in the right anterior insula and rostral aspects of the anterior cingulate cortex (ACC). Greater reductions in pain unpleasantness ratings were associated with greater activation of the orbitofrontal cortex (OFC) and thalamic deactivation (depicted in blue).