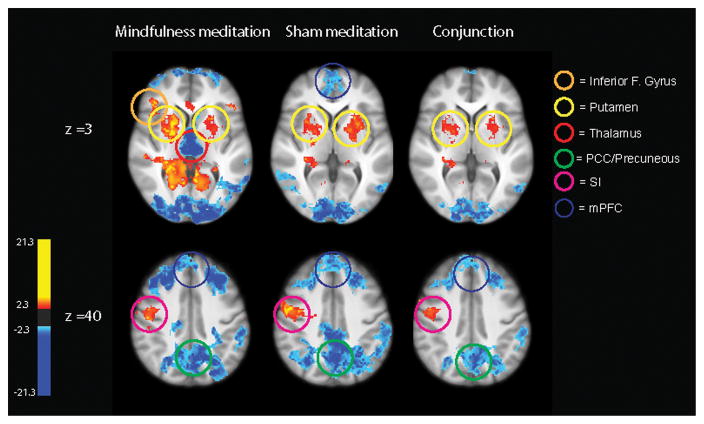
Figure 2.
The main effects of mindfulness meditation and sham mindfulness meditation involve similar neural processes. Mindfulness meditation and sham mindfulness meditation produced activation (red) in the bilateral putamen and primary somatosensory cortex (SI) corresponding to the nose/face regions and deactivation (blue) of the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) and precuneous/poster cingulate cortex (PCC). Mindfulness meditation also activated the right inferior frontal gyrus and produced deactivation of the bilateral thalamus. Conjunction analyses revealed significant overlapping activation in the bilateral putamen, SI representation of the nose/face, and deactivation of the PCC and mPFC.