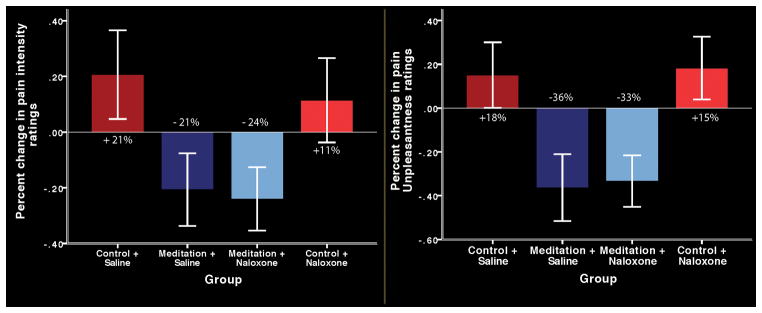
Figure 3.
Psychophysical pain intensity (left graph) and unpleasantness (right graph) ratings (95% confidence intervals). Meditation during saline (meditation + saline) infusion significantly (P < 0.001) reduced pain intensity and unpleasantness ratings compared with rest and the control and saline (control + saline) group. Naloxone did not reverse meditation-induced pain relief. Meditation during naloxone administration (meditation + naloxone) significantly (P < 0.001) reduced pain intensity and unpleasantness ratings compared with rest, the control + saline group, and the control and naloxone (control + naloxone) groups. There were also no significant differences in pain intensity or unpleasantness ratings between the meditation + saline and the meditation + naloxone groups (P > 0.69).