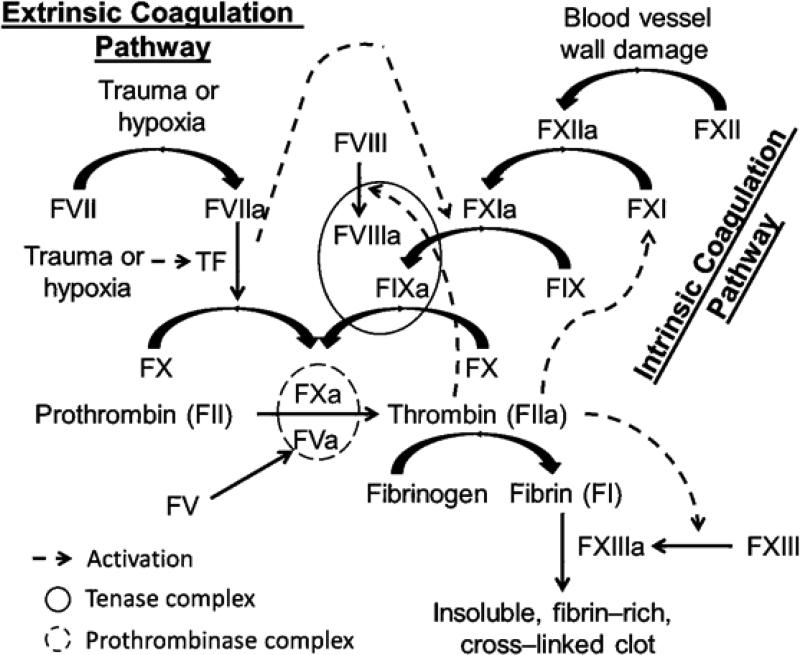
Figure 1.
An overview of the waterfall model coagulation cascade. Coagulation is triggered by either the extrinsic pathway or the intrinsic pathway, both lead into the common pathway that results in thrombin generation and the subsequent formation of insoluble, fibrin-rich, cross-linked clot. Natural anticoagulant proteins (not shown) include antithrombin (AT) which mainly inhibits thrombin and FXa, activated protein C (APC) which inhibits FVa and FVIIIa, and tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI) which mainly inhibits FXa. FXIa is a serine protease in the intrinsic pathway which gets activated by FXIIa and thrombin (in addition to auto-activation) to physiologically activates FIX to FIXa.