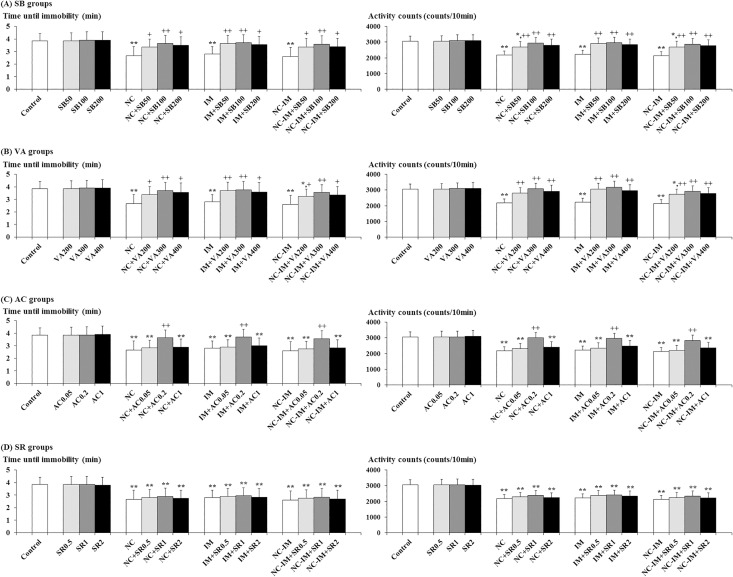
Fig 2. Antagonistic effects of histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors or cannabinoid type 1 (CB1) agonist against depression-like behaviors.
The parameter values of the forced swimming test at the 2 h time point after the last nicotine (NC) (0.8 mg/kg, s.c.) or immobilization stress (IM) (10 min) treatment are shown as means ± S.D. (n = 10) for each HDAC inhibitor or CB1 ligand co-treatment group (with each i.p. dose (mg/kg)). (A) Sodium butyrate (SB) co-treatment groups (SB groups); (B) Valproic acid (VA) co-treatment groups (VA groups); (C) ACPA (arachidonylcyclopropylamide; AC) co-treatment groups (AC groups); (D) SR 141716A (N-(Piperidin-1-yl)-5-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-4-methyl-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxamide hydrochloride; SR) co-treatment groups (SR groups). The data for the control, NC, IM, and NC plus IM (NC-IM) groups without any HDAC inhibitor or CB1 ligand co-treatments, as well as the HDAC inhibitor- and CB1 ligand-only groups, are also shown. * (p<0.05), ** (p<0.01): significant attenuation as compared to the control group; + (p<0.05), ++ (p<0.01): significant increase as compared to the NC, IM, or NC-IM group without any co-treatments.