Figure 4.
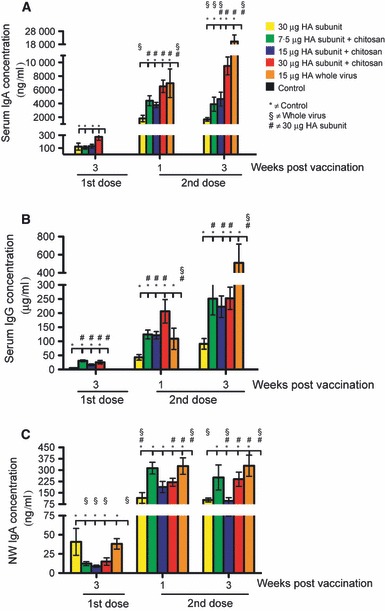
The serum and nasal wash antibody responses induced after intranasal influenza vaccination. Groups of five mice were intranasally immunised twice (21 days apart) with a subunit (SU) influenza A H5N1 vaccine. The control group consisted of unimmunised mice. Three groups were vaccinated with different antigen doses (7.5, 15 or 30 μg HA) of the chitosan‐adjuvanted SU vaccine. One group was vaccinated with a non‐adjuvanted SU vaccine with 30 μg HA, and a further group was immunised with a non‐adjuvanted 15 μg HA whole virus vaccine. Sera were collected at appropriate time points after the first and second immunisation and used to quantify the influenza‐specific serum IgG (B) and IgA (A) concentrations and the nasal wash (NW) IgA (C) concentrations using the ELISA. The data are presented as the mean antibody concentration of serum IgA (ng/ml) (A) and serum IgG (μg/ml) (B) and nasal wash IgA (ng/ml) (C) ± standard error of the mean. HA, haemagglutinin.
