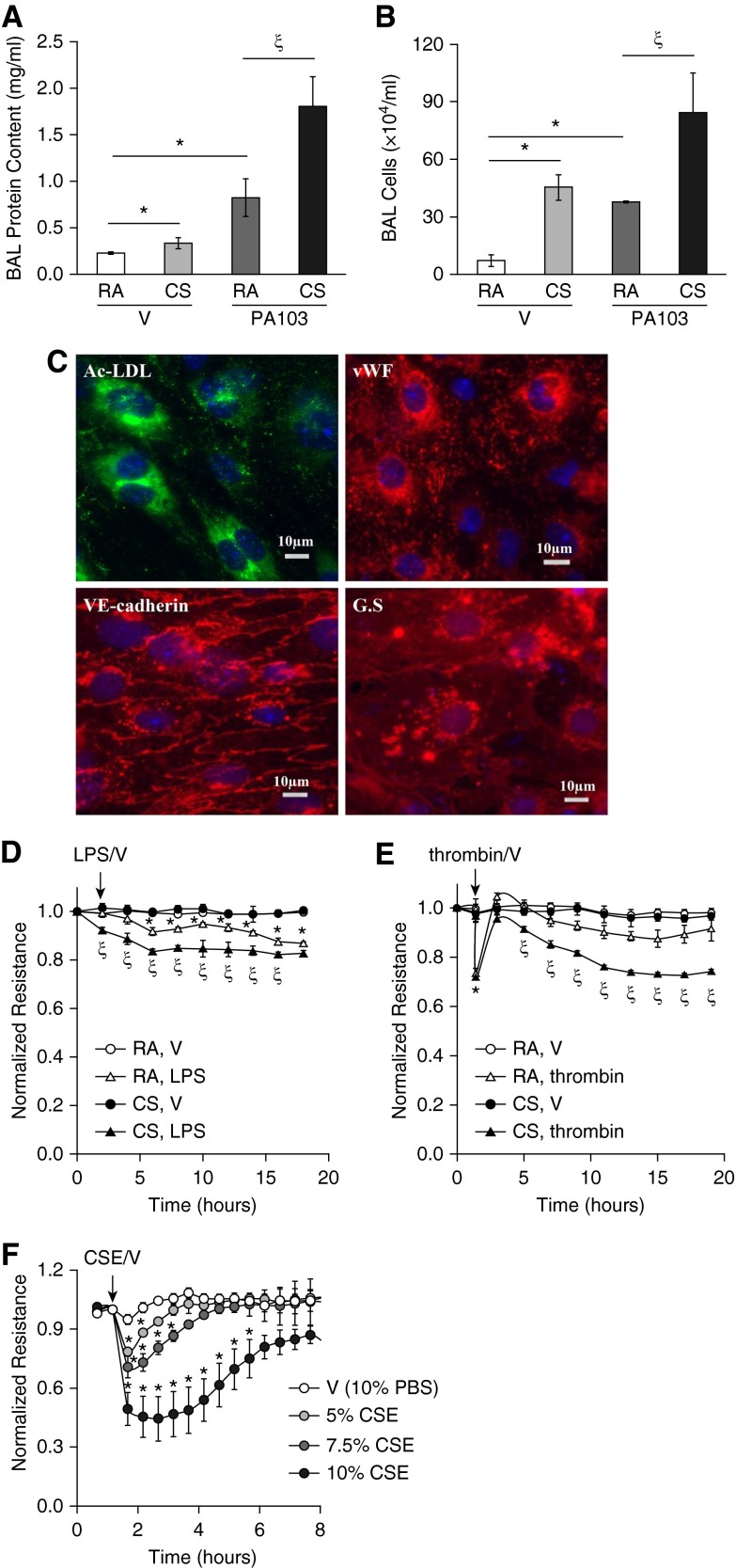
Figure 1.
Cigarette smoke (CS) exacerbated acute lung injury (ALI) in vivo and increased lung microvascular endothelial cell (LMVEC) permeability in vitro. (A and B) Male C57BL/6 mice (6–8 weeks old) were exposed to room air (RA) or CS for 6 hours. After 1 hour of rest, mice were intratracheally administered 5 × 103 CFU of Pseudomonas aeruginosa (PA103) or equal volume of saline as vehicle (V). 24 hours later, mice were killed and bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) protein levels and inflammatory cell counts were assessed. Four to six mice per group were used. The data are presented as the mean ± SE. ANOVA and Tukey-Kramer post hoc test was used to determine statistically significant difference across means among groups. *P < 0.05 versus (RA + V); ζP < 0.05 versus (RA + PA103); (C–E) 6-week-old male C57BL/6 mice were exposed to RA or CS for 6 hours. After overnight rest, LMVECs were isolated from cortical lung tissues, as described in Materials and Methods. A fraction of the isolated cells at passage (P) 1 were characterized by fluorescent microscopy (C) using EC markers, including acetylated low-density lipoprotein (Ac-LDL) uptake, von Willebrand factor (vWF), and vascular endothelial–cadherin, as well as LMVEC marker, Griffonia simplicifolia (GS) binding. The nuclei were counterstained with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole staining. Scale bars, 10 μm. Representative images from mice exposed to CS are shown. The remaining cells at P1 were plated onto electrical cell impedance sensor (ECIS) arrays at equal numbers of cells (2.5 × 105 cells/ well). After overnight attachment, cells were treated with vehicle (V), LPS (1 μg/ml), or thrombin (2 U/ml) for 20 hours and monolayer permeability was assessed by measuring electrical resistance across a monolayer using ECIS (D and E). Four independent experiments with duplicated ECIS wells for each condition each time were conducted. (F) Primary human LMVECs were treated with vehicle (V, 10% PBS) or varying concentrations of cigarette smoke extract (CSE) for indicated times, and monolayer permeability was assessed by ECIS. Three independent experiments with duplicated ECIS wells for each condition each time were conducted. For D–F, the data are presented as the mean ± SE of the normalized electrical resistance at the selected time points relative to their initial resistance. ANOVA and Tukey-Kramer post hoc test was used to determine statistically significant difference across means among groups. *P < 0.05 versus (RA + V) (D and E) or V (F); ζP < 0.05 versus (RA + LPS) (D) or (RA + thrombin) (E). Arrows indicate the time for addition of treatments.