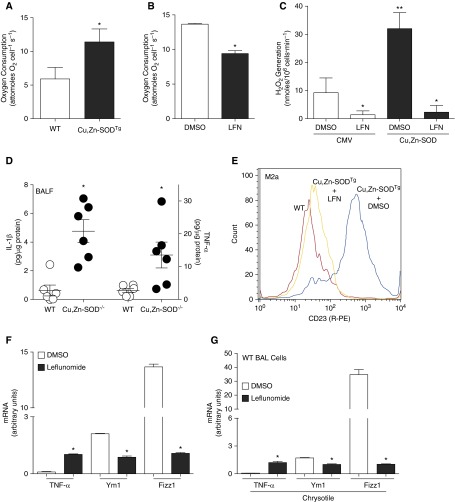
Figure 5.
Leflunomide (LFN) treatment decreases M2 polarization. (A) O2 consumption rate was determined in WT and Cu,Zn-SODTg BMDMs (n = 3); *P < 0.05. (B) WT BMDMs were treated with either vehicle control or LFN (200 μM). Oxygen consumption rate was determined (n = 4); *P < 0.05. (C) Macrophages were infected with adenoviral vector containing either an empty (CMV) or Cu,Zn-SOD construct. After 48 hours, cells were incubated with vehicle or LFN (200 μM). p-hydroxylphenyl acetic acid (pHPA) assay was performed, with results expressed as rate of H2O2 generation; *P < 0.05 versus dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and LFN (Cu,Zn-SOD), **P < 0.05 versus all other conditions (n = 3). (D) WT and Cu,Zn-SOD−/− mice were exposed to chrysotile (100 μg intratracheally). BAL was obtained after 21 days. IL-1β and TNF-α were measured by ELISA (n = 6); *P < 0.023. (E) BMDMs from WT, Cu,Zn-SODTg + DMSO, and Cu,Zn-SODTg + LFN were stained with R-PE–labeled anti-CD23 at a 1:10 dilution. Levels of CD23 were determined by flow cytometry. Representative of three histograms of CD23-stained macrophages is shown. (F) Macrophages were treated with either vehicle (DMSO) or LFN (200 μM) overnight. Total RNA from macrophages was isolated, and tnf-α, ym1, and fizz1 gene expression were measured. Results show arbitrary units normalized to β-actin mRNA (n = 4); *P < 0.05 versus DMSO. (G) WT mice were exposed to chrysotile asbestos (100 μg intratracheally). DMSO or LFN (1.4 mg/kg) was administered intraperitoneally every other day from Day 10. Mice were killed 21 days after exposure. Total RNA from alveolar macrophages was isolated, and tnf-α, ym1, and fizz1 gene expression was measured by quantitative RT-PCR. Results show arbitrary units normalized to β-actin mRNA (n = 4); *P < 0.05 versus DMSO. BALF, bronchoalveolar lavage fluid.