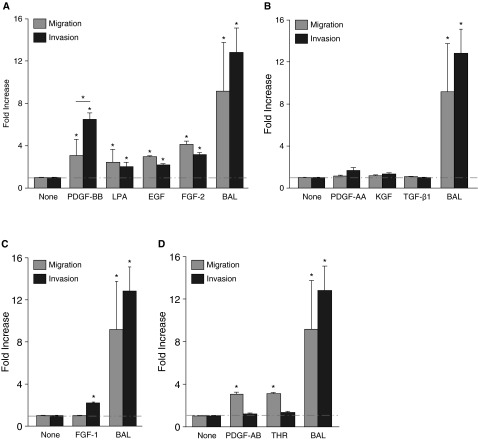
Figure 4.
Different effects of fibroblast-active mediators on migration versus invasion. Assessment of the migration and invasion of lung fibroblasts from unchallenged mice induced by multiple fibroblast-active mediators indicated that: (A) PDGF-BB, lysophosphatidic acid (LPA), epidermal growth factor (EGF), and fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF-2) induced both migration and invasion; (B) PDGF-AA, keratinocyte growth factor (KGF), and TGF-β1 induced neither migration nor invasion; (C) FGF-1 induced invasion, but not migration; and (D) PDGF-AB and thrombin induced migration but not invasion. BAL from mice at Day 7 after 1.2 U/kg bleomycin challenge induced greater invasion and migration than any individual mediator tested (A–D). The mediator concentrations used were 10−9 M PDGF-BB, 10−7 M LPA, 100 ng/ml EGF, 15 ng/ml FGF-2, 50 ng/ml PDGF-AA, 100 ng/ml KGF, 5 ng/ml TGF-β1, 20 ng/ml FGF-1, 10 ng/ml PDGF-AB, 10 ng/ml and thrombin, in serum-free Dulbecco’s modified Eagle's medium media, as determined by pilot dose–response studies (data not shown). Each of the panels shares the same BAL condition. Data are presented as mean (±SEM) fold increase in invasion, normalized to the cell-autonomous invasion of lung fibroblasts from unchallenged mice (n = 3 mice as the source of lung fibroblasts, and n = 3 as the source of BAL; *P < 0.05). THR, thrombin.