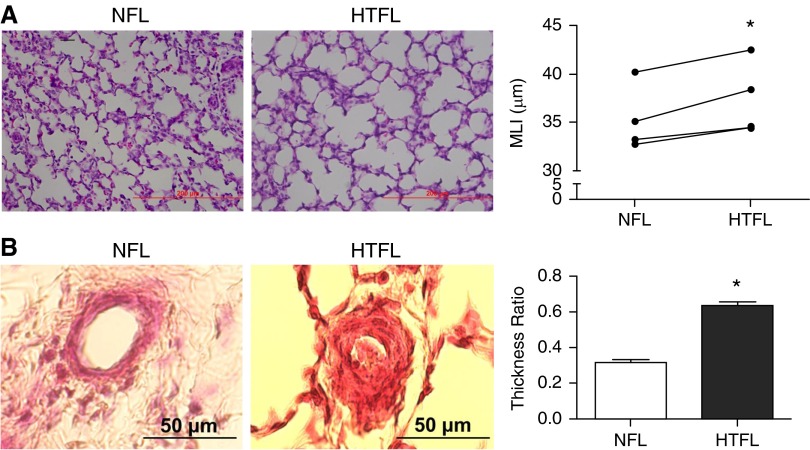
Figure 1.
Intrauterine pulmonary hypertension (hypertensive fetal lamb [HTFL]) impairs alveolarization and increases the smooth muscle cell layer thickness compared with normotensive co–twin fetal lung (NFL). (A) Mean linear intercept (MLI) in HTFL is higher than in NFL, indicating fewer and larger airspaces (individual data shown for n = 4). (B) The smooth muscle cell layer in HTFL pulmonary artery is thicker than in NFL (mean ± SEM; n = 3). *P < 0.05 compared with NFL. Scale bars: 200 μm in A and 50 μm in B.