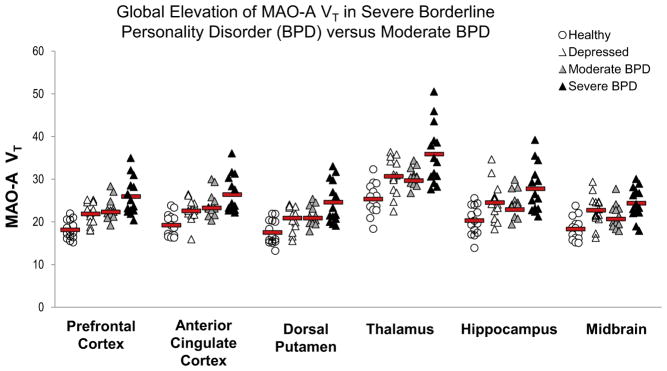
Figure 1.
Multivariate analysis of variance (MANOVA) indicates that severe BPD was associated with greater monoamine oxidase-A distribution volume (MAO-A VT) in both prefrontal and anterior cingulate cortex compared with the moderate BPD, depressed, and healthy groups (MANOVA group effect: F6,102 = 5.6, p < .001; least significant difference for severe BPD vs. other groups, p value range: <.001 to .024). Mean MAO-A VT was greater in severe vs. moderate BPD for each brain region sampled (p value range: .003 to .024). When the effect of group on MAO-A VT was evaluated across all regions, similar results were found (MANOVA group effect: F30,127 = 2.8, p = .002). Red bars indicate mean MAO-A VT values.