Fig. 3. Directed pneumococcal disease antigen assessment via the hybrid vector.
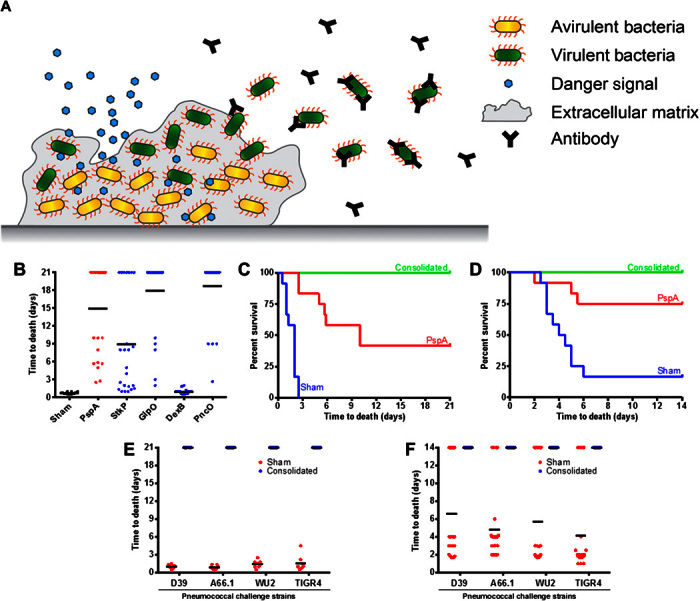
(A) Asymptomatic S. pneumoniae biofilm carriage is established in the nasopharynx and can be triggered (via signals such as viral infection) for virulent cellular release and dissemination characterized by extended tissue burden and disease. The antigens delivered with the hybrid vector were chosen to elicit a directed immune response to only the virulent subpopulation of S. pneumoniae. (B to D) Vaccine screening of individual virulent-specific antigens (x axis) (B) before consolidating the antigens to plasmids within the hybrid vector tested within sepsis (C) and pneumonia (D) disease challenge protection mouse model assays against the virulent S. pneumoniae strain D39. (E and F) Vaccination was extended to test other clinically relevant S. pneumoniae strains within sepsis (E) and pneumonia (F) challenge protection mouse models.
