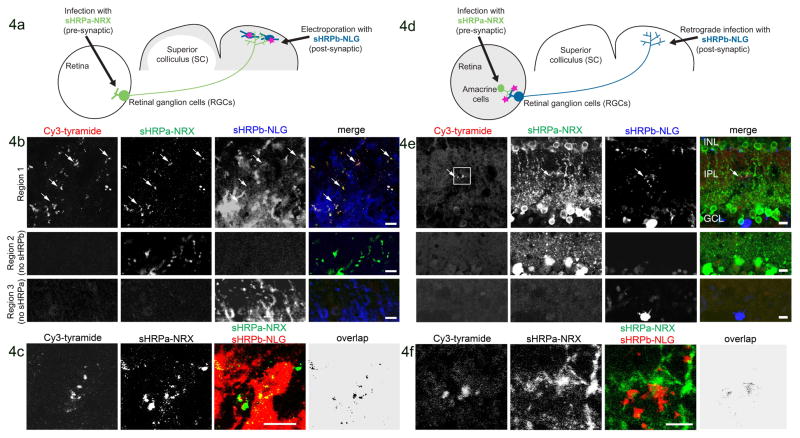
Figure 4. Detection of reconstituted sHRP in vivo.
A. Scheme for detection of anterograde contacts between RGCs and neurons of the SC.
B. Four weeks after mouse transduction as in (A), the SC was removed by dissection, incubated with heme, fixed, sectioned, and labeled with Cy3-tyramide, a fluorescent sHRP substrate. sHRPa-NRX and sHRPb-NLG expression were detected by staining with anti-HRP and anti-NLG antibodies, respectively (anti-HRP does not recognize sHRPb). The second and third rows show tissue regions lacking sHRPb or sHRPa, respectively. Arrows point to sHRP-stained terminals.
C. Labeled SC from a different animal. “Overlap” is the calculated overlap between sHRPa and sHRPb channels. This experiment was repeated 8 times with similar results.
D. Scheme for detection of retrograde contacts between RGCs and amacrine cells in the mouse retina. sHRPa-NRX expression was restricted to amacrine cells via use of a Cre line (see Methods).
E. One week after transduction as in (D), the retina was dissected and prepared as in (B). Second and third rows show tissue regions lacking sHRPb or sHRPa expression, respectively. Arrow points to sHRP staining. Box indicates the region shown in (F).
F. Zoom region indicated by the box in (E). All scale bars, 10 μm.