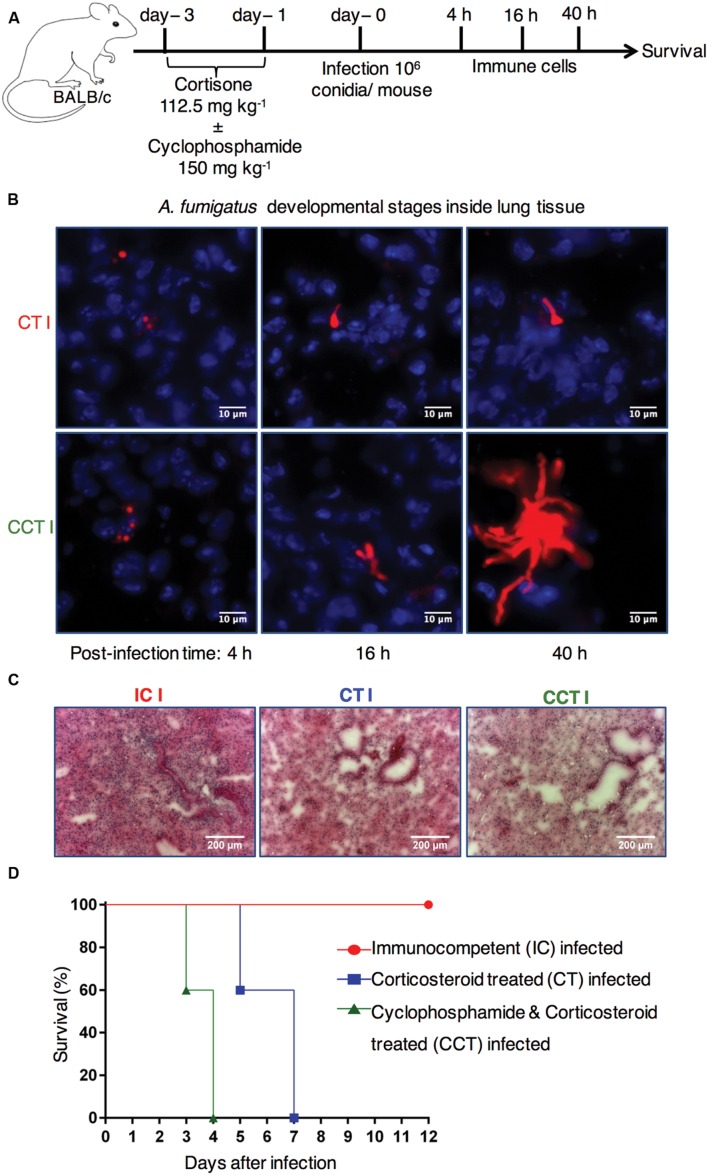
FIGURE 1.
Immunocompromised mouse models to investigate the dynamic host immune response and survival after Aspergillus fumigatus infection. (A) Experimental setup. BALB/c mice were treated with hydrocortisone (112.5 mg kg-1) on day -3 and day -1 (CT mice) or with cyclophosphamide (150 mg kg-1) and hydrocortisone (112.5 mg kg-1) on day -3 and day -1 before A. fumigatus infection (CCT mice). On day 0 mice were intranasally infected with 1 × 106 conidia/mouse. Pulmonary immune cell and cytokine responses were analyzed at 4, 16, and 40 h post infection (p.i.). Survival was followed for 12 days p.i. (B) A. fumigatus developmental stages inside lung tissue. Immunofluorescence microscopy of lungs from immunosuppressed mice that were infected with Afu-TdTomato conidia at 4, 16, and 40 h p.i. Upper panel CT mice and lower panel CCT mice, A. fumigatus in red color and 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) staining for nuclei in blue color. Scale bar 10 μM. (C) Lung immune cell infiltration in IC, CT, and CCT infected mice: Lung sections were stained with hematoxylin & eosin at 40 h p.i. and imaged in bright field microscope. Scale bar 200 μM. (D) Survival of mice under different immunosuppressive regimens: immunocompetent infected (IC infected), corticosteroid treated and infected (CT infected), and cyclophosphamide and corticosteroid treated and infected (CCT infected); (n = 5/group). Immunocompetent mice (IC) are resistant to infection, whereas CT (P = 0.0004) and CCT (P < 0.0001) mice succumb to invasive aspergillosis. However, CT mice survive infection significantly longer than CCT mice (P < 0.0001). When mice lost ≥20% weight, they reached an experimental end point and were euthanized according to animal ethics regulations. Log-rank (Mantel–Cox) test was utilized to determine differences in survival.