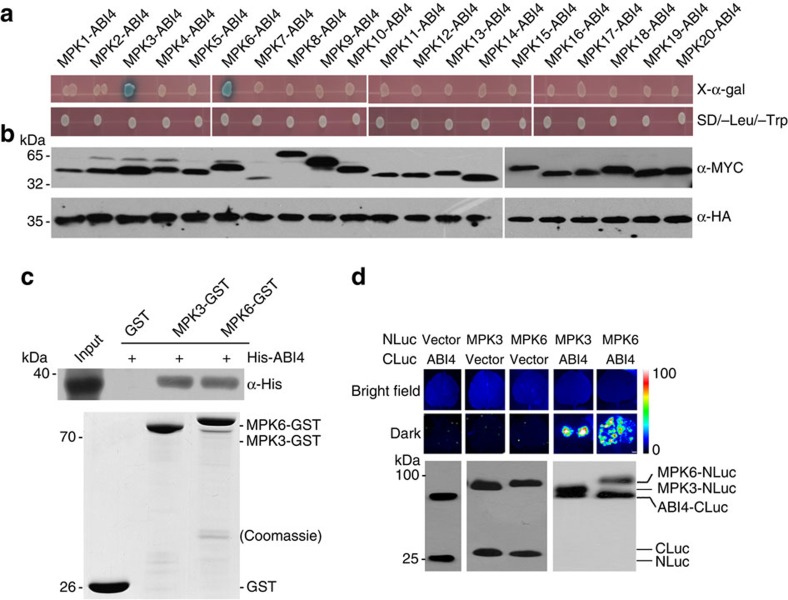
Figure 1. ABI4 interacts with MPK3 and MPK6.
(a) Yeast two-hybrid assay for the interaction between ABI4 and MPK3/MPK6. Fusion constructs of the ABI4 (amino acids 1–160) fused with the GAL4 DNA-binding domain (BD) and 20 MAPKs fused with the GAL4 activation domain (AD) were co-transformed into Y2H Gold yeast cells. These strains were grown on SD-Leu-Trp medium (bottom) and subjected to α-galactosidase assay (top). (b) Immunoblot analysis of target fusion proteins in the yeast two-hybrid assays indicated in (a) using HA tag and Myc tag antibodies, respectively. (c) Pull-down assay for the interaction of ABI4 with MPK3/MPK6. His-tagged ABI4 was incubated with immobilized GST or GST-tagged MPK3/MPK6. After washing, bound proteins were eluted and subjected to immunoblot analysis using an antibody against His. Coomassie blue (CBB) staining indicates equal amounts of bait proteins. (d) Luciferase complementation imaging assay for the interaction of ABI4 with MPK3/MPK6. N. benthamiana leaves were co-infiltrated with the agrobacterial strains harbouring the construct pairs of ABI4-CLuc and MPK3/MPK6-NLuc. ABI4-CLuc and NLuc as well MPK3/MPK6-NLuc and CLuc were used as controls. The images were taken after 48 h of infiltration. Bright luminescence indicates direct protein–protein interactions and the pseudocolour bar shows the range of luminescence intensity in the images. The western blot below shows the expression levels of CLuc- and NLuc-fusion proteins using anti-full-length firefly LUC antibody. Scale bar, 1 cm.