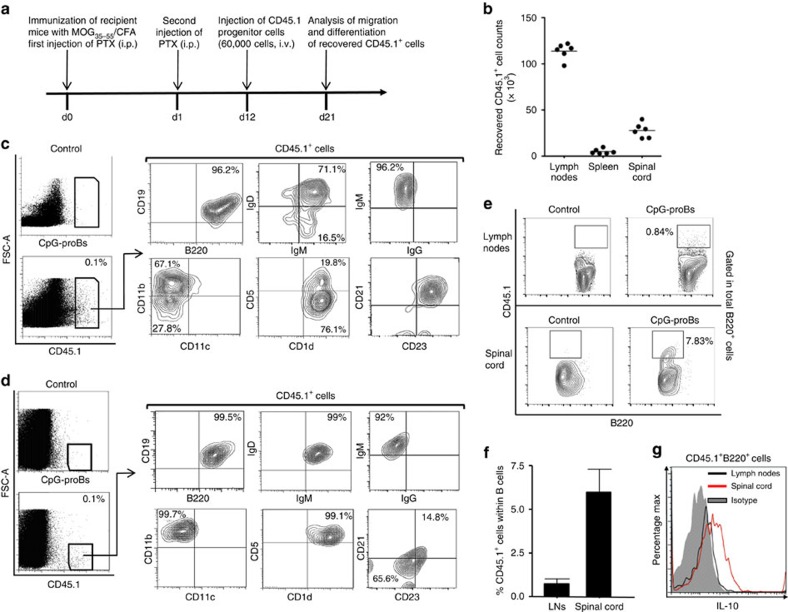
Figure 3. Phenotypic characterization of CD45.1+ cells recovered from reactive LNs and spinal cord.
(a) Experimental protocol: EAE disease was induced in CD45.2 C57BL/6J mice which then were injected at day 12 of the disease with CpG-proB cells, prepared from the BM of congenic CD45.1+ C57BL/6J and stimulated with CpG-B for 18 h. The recovery (b) and differentiation status (c–e) of CD45.1+ injected cells were analysed at day 21. (b) Absolute CD45.1+ cell counts recovered within reactive LN, spleen and spinal cord of injected mice at day 21 after immunization, that is, at the peak of the disease, n=6 mice per group. (c) Flow cytometry analysis of the frequency of CD45.1+ cells recovered in reactive LN at day 21, and of the frequency of gated CD45.1+ cells expressing the B-cell markers B220, CD19, IgM, IgD, IgG, as well as the markers CD5 and CD1d, CD11b, and CD11c, CD21 and CD23. (d) Flow cytometry analysis of the frequency of the CD45.1+ progeny of CpG-proB cell recipients, recovered within the spinal cord of CpG-proB-injected mice at day 21 of the disease, expressing B220, CD19, IgM, IgD, IgG, CD5, CD1d, and CD11b, CD11c, CD21 and CD23. (e,f) Frequency of CD45.1+ cells derived from injected CpG-proBs gated within total B220+ cells in a representative experiment (e) and as mean±s.e.m. of three determinations (f). (g) Frequency of IL-10-producing CD45.1+ cells in spinal cord and reactive LN, determined by intracellular flow cytometry as shown in the ‘Methods' section.