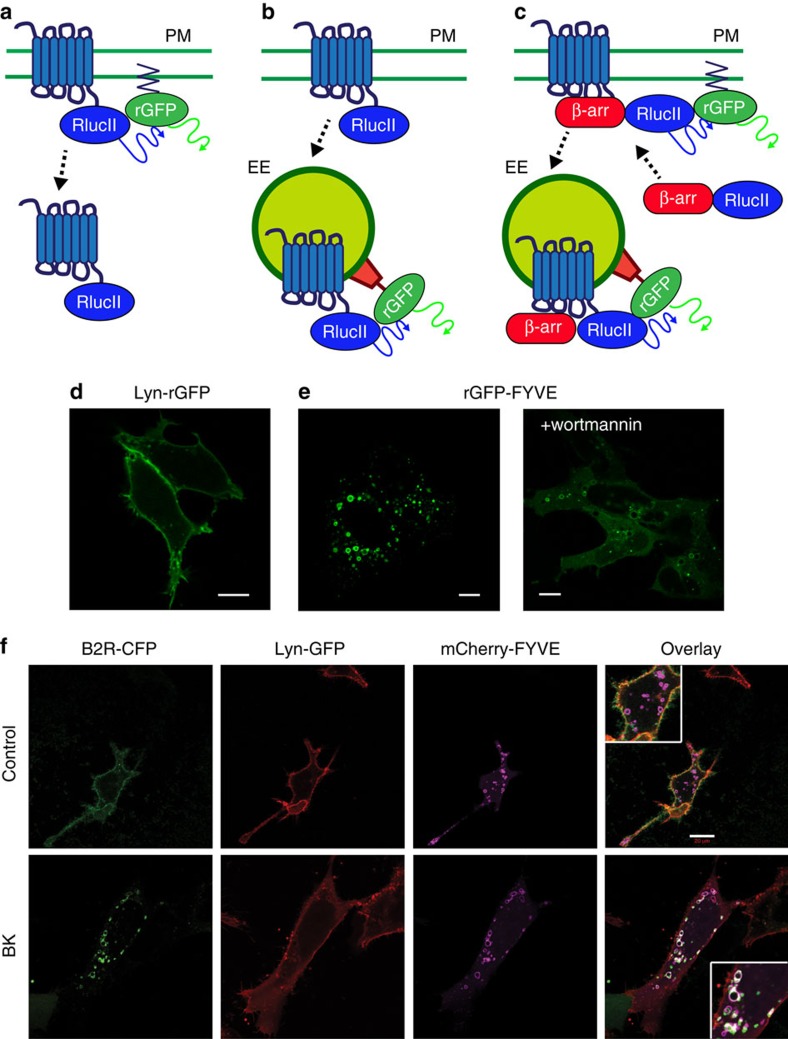
Figure 1. Characterization of EbBRET-based trafficking sensors.
(a–c) Illustration of three BRET-based sensor configurations for monitoring GPCR and β-arrestin trafficking. (a) To monitor the receptor amount at the plasma membrane (PM), rGFP was anchored at the PM by tagging the acylation motif of Lyn-kinase (MGCIKSKGKDS) to the N terminus of rGFP. (b,c) To examine the targeting of receptor (b) or β-arrestin (c) to the early endosome (EE), the FYVE domain of endofin (Q739-K806), which tethers the sensor in the EE, was fused to the C terminus of rGFP. The PM- and EE-targeted rGFP are the EbBRET acceptor for RlucII-tagged GPCRs and β-arrestin donors. (d,e) Confocal fluorescence microscopy of HEK293 cells expressing either Lyn-rGFP (d) or rGFP-FYVE (e). rGFP-FYVE expressing cells were treated with 500 nM wortmannin for 40 min (e, right panel). (f) Validation of the subcellular localization of the PM-targeted Lyn and EE-targeted FYVE domains during receptor endocytosis. Confocal fluorescence microscopy of HEK293 cells transiently expressing B2R-CFP, Lyn-GFP10 and mCherry-FYVE. Top panels: basal condition (control); bottom panels: following a 15-min stimulation with 1 μM bradykinin (BK). For enhanced co-localization visualization, pseudo colours for B2R-GFP (green), Lyn-GFP10 (red) and mCherry-FYVE (purple) were applied. Scale bars, 10 μm (d,e) and 20 μm (f).