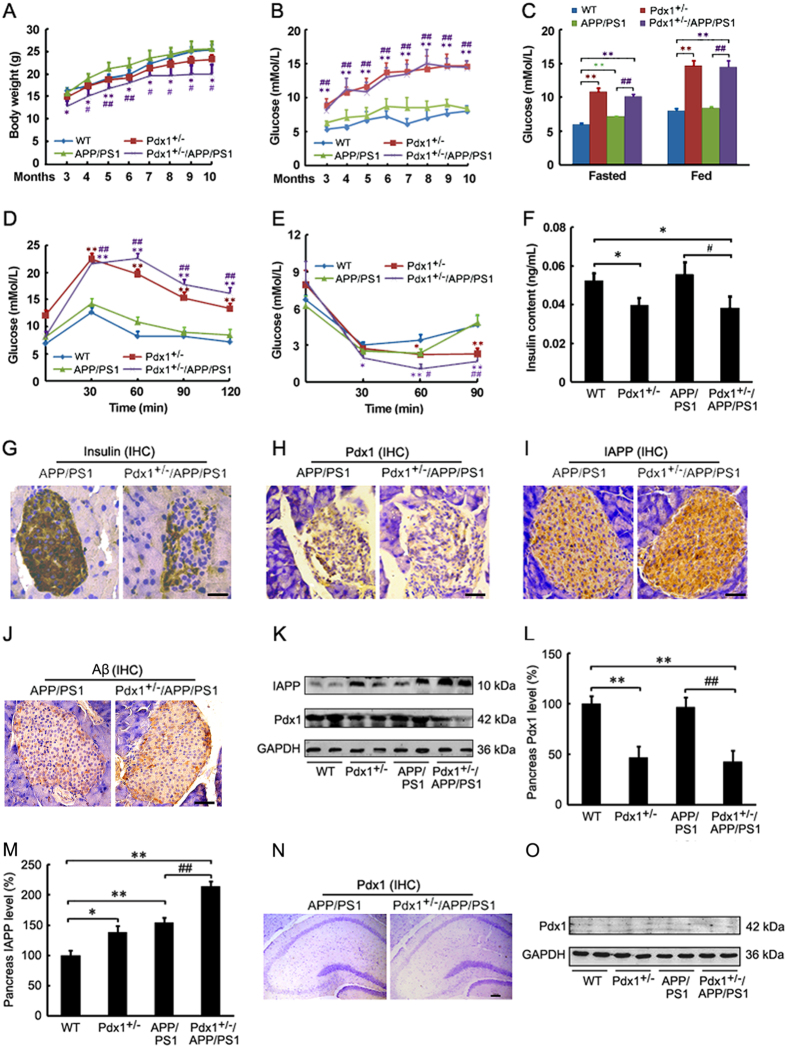
Figure 1. Metabolic features of Pdx1+/−/APP/PS1 mice.
(A,B) Ponderal growth and randomly blood glucose changes in 3- to 10-month-old WT, Pdx1+/−, APP/PS1 and Pdx1+/−/APP/PS1 mice. (C) Blood glucose levels at 41 weeks of age. (D) Glucose levels following intraperitoneal injection of 2 g/kg glucose at 12 weeks of age. (E) Blood glucose levels during an ITT (0.75 U/kg, 13-week-old mice). (F) Serum insulin concentrations at 41 weeks of age. (G–J) Pancreatic sections were stained with antisera against insulin/Pdx1/IAPP/Aβ in islets from 10-month-old APP/PS1 and Pdx1+/−/APP/PS1 mice for immunohistochemistry. Scale bar = 25 μm. (K–M) Western blot analysis showed that the Pdx1 levels were decreased, whereas the IAPP levels were markedly increased in the Pdx1+/−/APP/PS1 mouse brain compared with the APP/PS1 mouse brain. GAPDH was used as an internal control. (N,O) Immunohistochemistry and Western blot results showed that the Pdx1 protein had not been observed in the hippocampus of mice. Data represent the mean ± S.E. (n = 10). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 compared with the WT control group; #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01 compared with the APP/PS1 group.