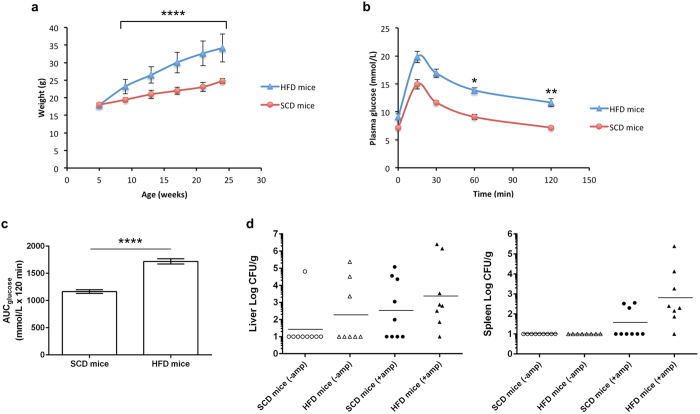
Figure 5. Incidence of extraintestinal infection was not significantly different between obese/glucose intolerant mice and healthy mice upon oral inoculation with hvKP K1.
Data in (a–c) are means ± SEM. (a) Weight of mice fed a SCD or HFD over a course of 19 weeks. Ampicillin treatment between weeks 16 to 19 did not alter body mass. (b) Plasma glucose concentrations during the OGTT following 6 hours of fasting in mice fed a SCD or HFD for 16 weeks. Percentage change from basal (fasting glucose level at 0 min) in SCD-fed mice: 15 min = + 107.6% ± 10.0, 30 min = + 64.0% ± 6.3, 60 min = 26.7% ± 5.5, 120 min = + 1.1% ± 5.3. Percentage change from basal in HFD-fed mice: 15 min = + 121.2% ± 15.8, 30 min = + 88.8% ± 12.3, 60 min = 54.9% ± 8.8, 120 min = + 28.5% ± 5.4. Glucose elimination is significantly faster in SCD-fed than HFD-fed mice (P = 0.012 and 0.003 by Student’s t test, when comparing percentage change at 0–60 minutes and 0–120 minutes, respectively). (c) Area under the curve for glucose in (b), calculated using the trapezoidal rule. (d) Bacterial burden in the extraintestinal organs of SCD-fed (healthy) and HFD-fed (obese/glucose intolerant) mice that were treated with ampicillin or not, upon oral infection with 108 CFUs of the K1 strain SGH04. Each dot represents one infected mouse, whose liver and spleen were harvested 72 hours post-infection. Horizontal bars indicate geometric means. Tissue homogenates that yielded no colonies were plotted with the value 10 CFU/g, which is the approximate limit of detection.