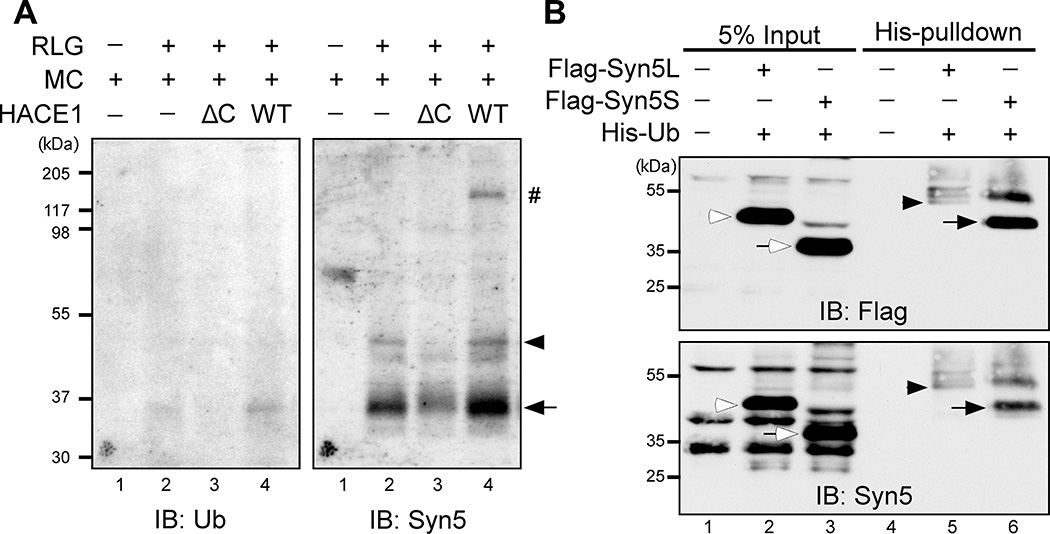
Figure 1. Syn5 is monoubiquitinated in mitosis.
(A) Identification of Syn5 as a substrate of HACE1. Purified rat liver Golgi (RLG) membranes were mixed with mitotic cytosol (MC), recombinant WT HACE1 or ΔC mutant, and His-ubiquitin. After incubation, re-isolated membranes were solubilized in detergent, ubiquitinated proteins were isolated by Ni-NTA affinity purification and analyzed by Western blot with antibodies to ubiquitin (left panel) and Syn5 (right panel). Shown are representative results from four independent experiments. Note that the signals for both short (Syn5S, arrow) and long (Syn5L, arrowhead) forms of Syn5 were highly detectable when Golgi membranes were incubated with mitotic cytosol alone that contains endogenous HACE1 (lane 2), but the intensity was significantly reduced by HACE1 ΔC (lane 3) and enhanced by WT HACE1 (lane 4). The Syn5 antibody was generated by a GST fusion protein, and thus recognizes copurified GST-HACE1 (indicated by #).
(B) HeLa cells co-transfected with Syn5 (Flag-Syn5L or Flag-Syn5S) and His-Ubiquitin (His-Ub) were synchronized to mitosis followed by Ni-NTA affinity purification and Western blot for Flag and Syn5. Note that both the long and short forms of Syn5 are ubiquitinated, displaying an 8 kD shift: Syn5S (empty arrow) in lane 3 vs. Syn5S-ub (solid arrow) in lane 6; and Syn5L (empty arrowhead) in lane 2 vs. Syn5L-ub (solid arrowhead) in lane 5.
See also Figure S1.