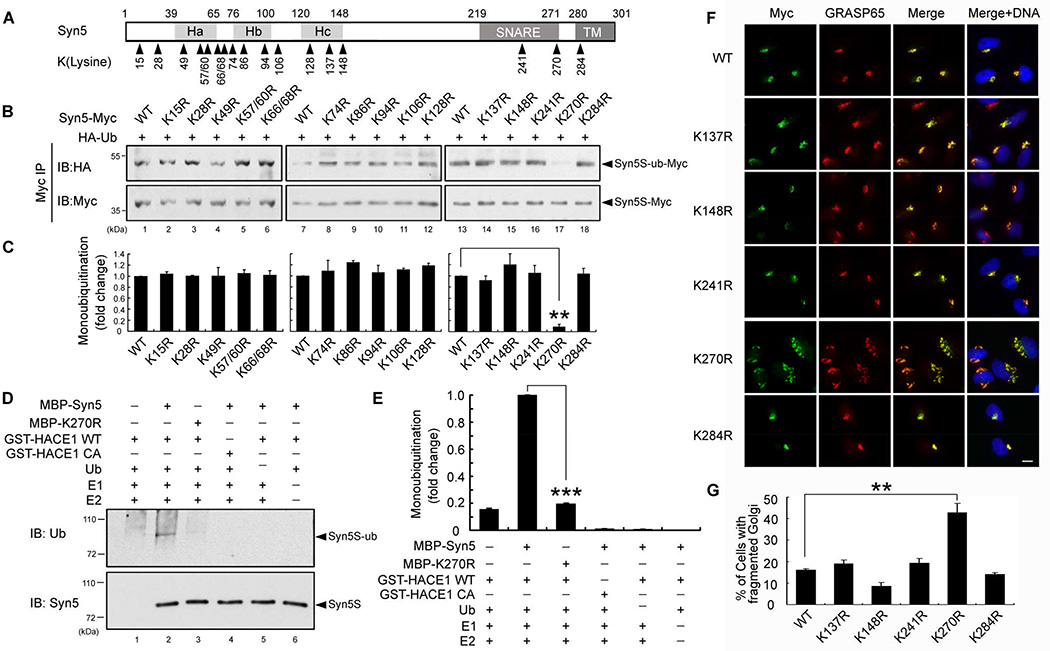
Figure 4. Syn5 is ubiquitinated on lysine 270.
(A) Schematic representation of Syn5 short form. Syn5 possesses a three helical bundle (consisting of Ha, Hb and Hc regions), a SNARE motif and a transmembrane (TM) domain. The 17 lysines conserved between rat and human are indicated.
(B–C) Mutation of K270 reduces Syn5 monoubiquitination. (B) HeLa cells were co-transfected with Syn5-Myc or the indicated KR mutant and HA-Ub, synchronized to mitosis, immunoprecipitated by anti-Myc and blotted for HA-Ub and Syn5-Myc. (C) Quantitation of (B) from three independent experiments.
(D) K270R mutation reduces Syn5 ubiquitination in vitro. Indicated proteins were mixed and incubated followed by Western blotting for ubiquitin. Note the reduced ubiquitin signal for K270R compared to WT Syn5 (lane 3 vs. 2).
(E) Quantitation of the ubiquitin signal in (D) from three independent experiments.
(F) Expression of the K270R mutation results in Golgi fragmentation. Representative fluorescence images of HeLa cells transfected with indicated Syn5 constructs and stained for Myc (Syn5-Myc) and a Golgi marker GRASP65. Note the fragmented Golgi in K270R-expressing cells. Scale bar, 10 µm.
(G) Quantitation of (F) from three independent experiments.
Data are represented as mean ± s.e.m. *, p < 0.05**; p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001.
See also Figure S3–S4.