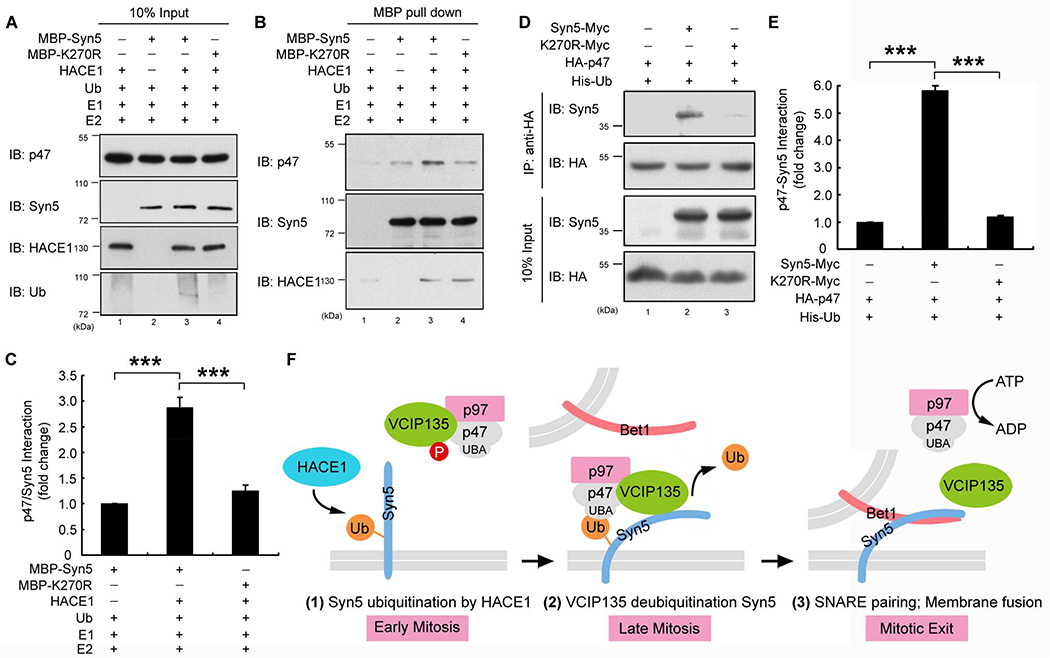
Figure 7. Syn5 ubiquitination increases its interaction with p47.
(A–C) Syn5 ubiquitination enhances Syn5-p47 interaction in vitro. MBP-Syn5 was pulled down after in vitro ubiquitination reaction and further incubated with recombinant p47 (A). After re-isolation of Syn5, bound p47 was assessed by Western blot (B). (C) Quantitation of p47 bound to MBP-Syn5 in (B) from three independent experiments.
(D) Syn5 ubiquitination enhances Syn5-p47 interaction in vivo. HeLa cells expressing indicated constructs were synchronized in mitosis and immunoprecipitated with an anti-HA antibody and blotted for both Syn5-Myc and HA-p47.
(E) Quantitation of p47-Syn5 interaction in (D) from three independent experiments.
(F) A hypothetic model for the role of Syn5 ubiquitination in p97/p47-mediated post-mitotic Golgi membrane fusion. In early mitosis (left panel), Syn5 is monoubiquitinated by HACE1 on the Golgi membranes, while VCIP135 is inactivated by mitotic phosphorylation. Syn5 recruits p97/p47 complex and VCIP135 to the Golgi membranes through the interaction between the ubiquitin moiety on Syn5 and the UBA domain of p47 (middle panel). In late mitosis, ubiquitin on Syn5 is removed by VCIP135 that is reactivated by dephosphorylation, enabling Syn5-Bet1 SNARE complex formation and thus membrane fusion by p97 at mitotic exit (right panel).
Data are represented as mean ± s.e.m. ***, p < 0.001.