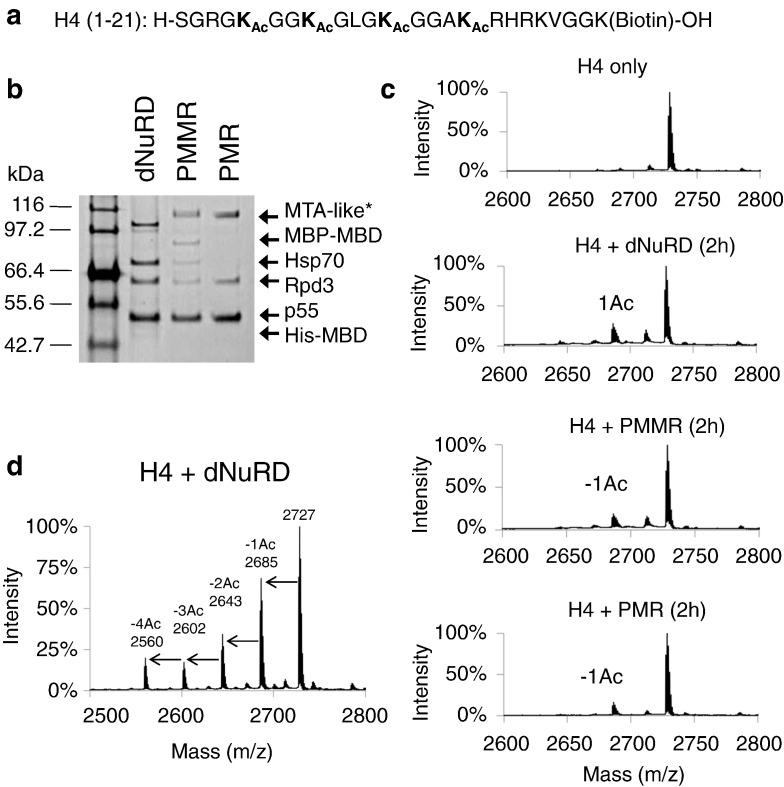
Fig. 4.
Deacetylase activity of NuRD complexes. (a) A synthetic peptide corresponding to the N-terminal 21 amino acids of histone H4 was used as substrate for the deacetylation assays. The amino acid sequence is shown with acetylated lysine residues indicated (5, 8, 12, and 16; Ac, acetylated lysine ε-amino group). A biotin tag is present at the C-terminus. (b) SDS-PAGE section from a NuPAGE Bis-Tris gradient mini gel (4%–12%) showing that the concentration of endogenous (dNuRD) and recombinantly produced PMR and PMMR complexes is similar in all the assays. Recombinant MTA-like protein with the oligohistidine-triple FLAG epitope tandem affinity purification tag (marked with an asterisk) migrates at a higher molecular weight than endogenous MTA-like. A minor contaminant in the PMMR preparation was identified as Hsp70. (c) The deacetylase activity of dNuRD, PMR and PMMR complexes was assessed by MALDI-TOF MS analysis of the acetylated peptide substrate. Deacetylase reactions were terminated by addition of acid after 2 h incubation and analyzed by MALDI-TOF. H4, tetra-acetylated histone H4 (1–21) peptide; − 1Ac, H4 (1–21) peptide with one acetyl group removed. (d) MALDI-TOF analysis after an overnight deacetylation reaction of tetra-acetylated histone H4 (1–21) peptide by the dNuRD complex. Substrate peptides lacking up to four acetyl groups (complete deacetylation) are detected.