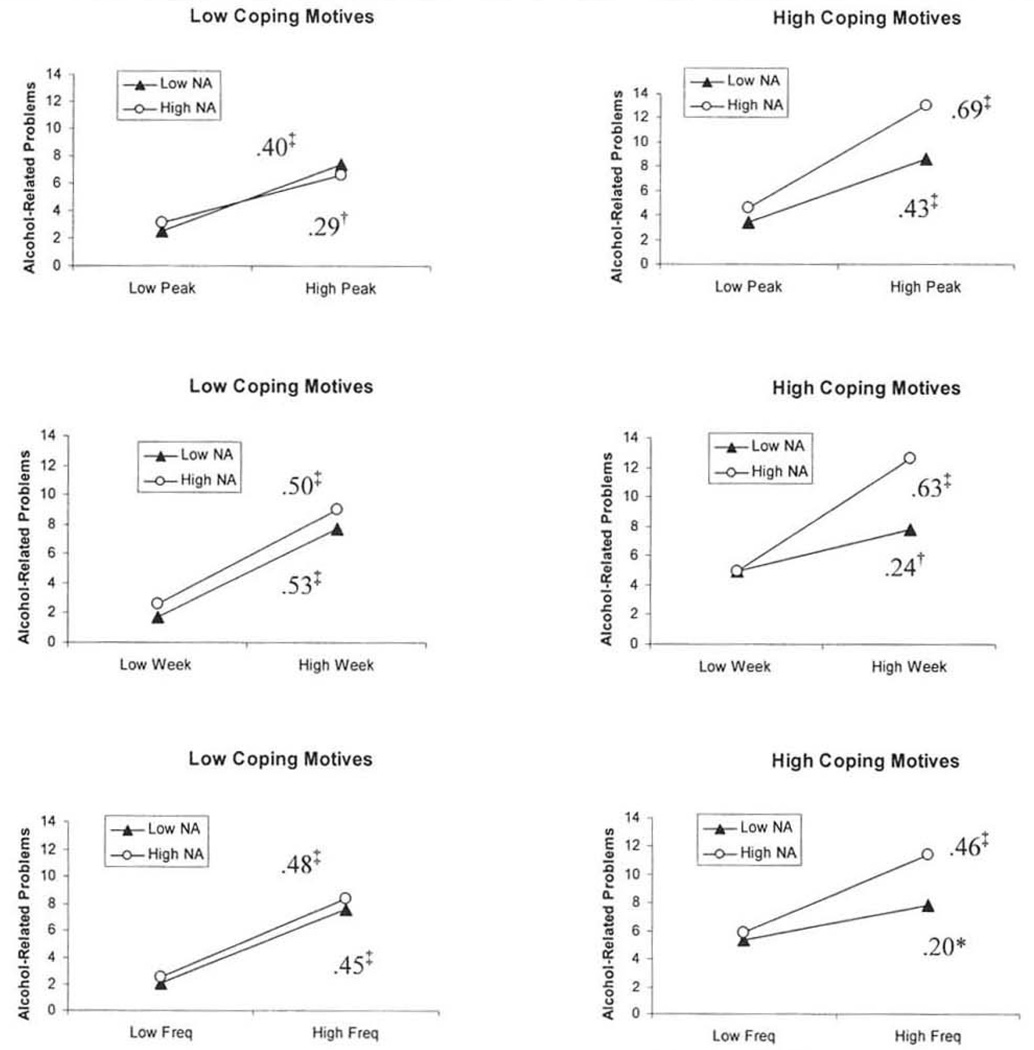
Figure 1.
The three-way interaction among coping motives, negative affect, and alcohol consumption in relation to alcohol-related problems. Values represent standardized beta weights. Peak represents maximum number of drinks consumed on one occasion in the previous month. Week represents the average number of standard drinks consumed per week over the past month. Freq = the average number of days per week in which alcohol was consumed over the previous month: NA = negative affect.
*p < .05; †p < .01; ‡p < .001.