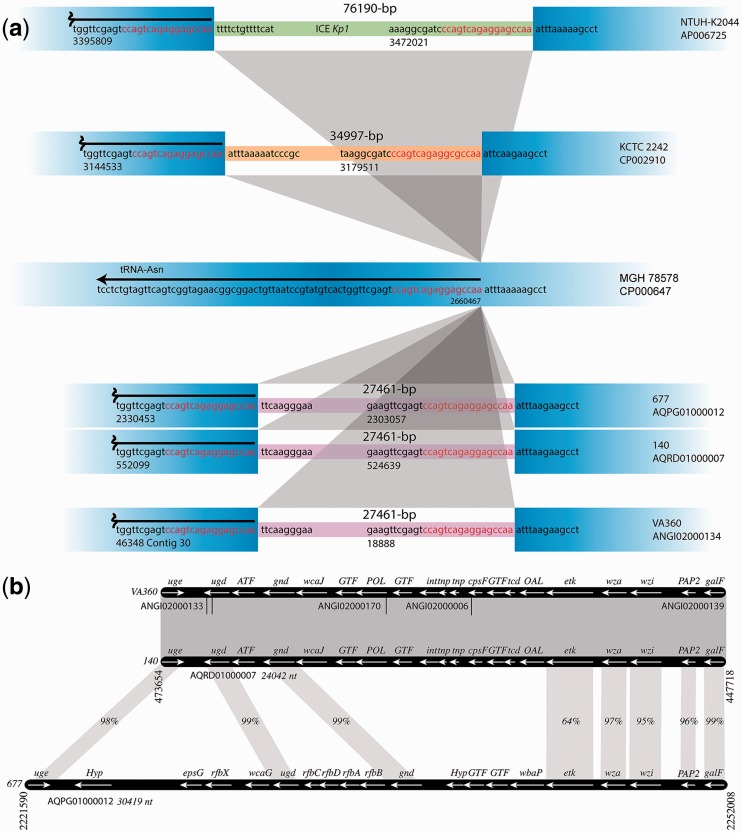
Fig. 2.—
HHZ Regions 3 and 4. (a) Schematic diagram of the Region 3 within the HHZs of several K. pneumoniae strains. The DNA sequences surrounding the hot spot and inserted fragments are represented in blue. The inserted regions are shown in thinner lines with different colors to indicate that the sequences are different. The sequences inserted in strains Kb140, Kb677, and VA360 are identical. The coordinates are those found in GenBank. The hot spot sequences, also known as attO (Lin et al. 2008), are red and the sequences immediately adjacent to the hot spots are black. In the case of strain NTUH-K2044 the inserted sequenced is the ICEKp1 pathogenicity island. (b) Schematic comparison of the Region 4, which consists of the CPC, within the HHZs of K. pneumoniae strains Kb140, Kb677, and VA360. Grayed regions represent high homology. In those cases where there is no 100% identity, the identity percentage is shown. In the case of strain VA360, the Region 4 was put together using different contigs, which are identified by their accession numbers. Coordinate numbers are those in GenBank. Potential function of genes (Kelly and Whitfield 1996; Whitfield 2006; Shu et al. 2009): uge, UDP-galacturonate 4-epimerase; ugd, UDP-glucose dehydrogenase; ATF, acyl transferase; gnd, gluconate-6-phosphate dehydrogenase; wcaJ, undecaprenyl-phosphate glycosyltransferase; GTF, glycosyl transferase; POL, polysaccharide biosynthesis; int, integrase-like; tnp, transposase-like; cpsF, CMP-N-acetylneuraminic acid synthetase; tcd, glycosyltransferase; OAL, O-antigen ligase; etk, tyrosine-protein kinase; wza, polysaccharide export lipoprotein; wzi, integral outer membrane protein; PAP2, PAP2 superfamily; galF, modulator of GalU to elevate the cellular concentration of UDP-glucose; Hyp, hypothetical; epsG, putative capsular polysaccharide biosynthesis protein; rfbX (wzx), flippase; wcaG, GDP-4-keto-6-deoxy-D-mannose 3,5-epimerase/reductase; rfbAB, ATP-binding cassette transporter; rfbC, involved in polysaccharide synthesis (epimerase), rfbD, involved in polysaccharide transport; wbaP, membrane protein that helps transfer a galactose residue from UDP-Gal to undecaprenol diphosphate to form Gal-p-UndP.