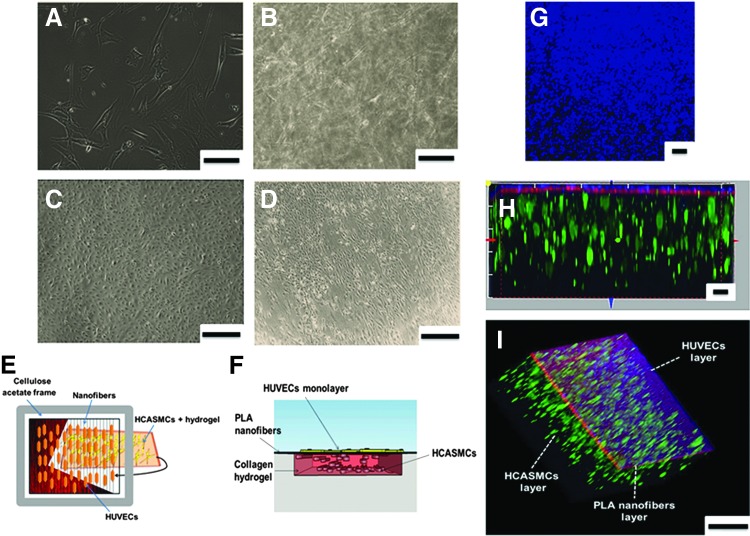
FIG. 2.
The morphology and assembly of the cells within the intimal and medial layer constructs. (A) Typical brightfield image of HCASMCs in monolayer culture. (B) Brightfield image of HCASMCs seeded and cultured in type I collagen hydrogel for 10 days. (C) Brightfield image of HUVECs in monolayer culture showing a typical cobblestone morphology of HUVECs. (D) Brightfield image of HUVECs in a full tissue-engineered blood vessel construct cultured for 4 days. The cells were grown on top of high-density, rhodamine-labeled aligned PLA nanofibers supported by a medial layer. (E) A diagrammatic representation of a top view of a multilayered TEBV construct and its assembly. (F) Side view sketch of the TEBV construct showing the locations of the cells within the construct. (G) An upper view image of fluorescently tracked HUVEC layer of the TEBV. (H, I) Side and luminal view images of the three distinct layers of TEBV construct. HUVECs (blue), PLA nanofibers (red), and HCASMCs (green). Scale bar (A, B) 150 μm; (C, D) 400 μm; (G–I) 30 μm. HCASMC, human coronary artery smooth muscle cell; HUVEC, human umbilical vein endothelial cell; TEBV, tissue engineering blood vessel. Color images available online at www.liebertpub.com/tec